Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
∆ABD is a right triangle right-angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that
(i) AB2 = BC x BD
(ii) AC2 = BC x DC
(iii) AD2 = BD x CD
(iv) `"AB"^2/"AC"^2="BD"/"DC"`
Solution
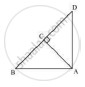
(i) In ΔADB and ΔCAB
∠DAB = ∠ACB = 90°
∠ABD = ∠CBA (common angle)
∠ADB = ∠CAB (remaining angle)
So, ΔADB ~ ΔCAB (by AAA similarity)
Therefore `"AB"/"CB"="BD"/"AB"`
⇒ AB2 = CB × BD
(ii) Let ∠CAB = x
In ΔCBA
∠CBA = 180° − 90° − 𝑥
∠CBA = 90° − 𝑥
Similarly in ΔCAD
∠CAD = 90° − ∠CAD = 90° − 𝑥
∠CDA = 90° − ∠CAB
= 90° − 𝑥
∠CDA = 180° −90° − (90° − 𝑥)
∠CDA = x
Now in ΔCBA and ΔCAD we may observe that
∠CBA = ∠CAD
∠CAB = ∠CDA
∠ACB = ∠DCA = 90°
Therefore ΔCBA ~ ΔCAD (by AAA rule)
Therefore `"AC"/"DC"="BC"/"AC"`
⇒ AC2 = DC × BC
(iii) In ΔDCA & ΔDAB
∠DCA = ∠DAB (both are equal to 90°)
∠CDA = ∠ADB (common angle)
∠DAC = ∠DBA (remaining angle)
ΔDCA ~ ΔDAB (AAA property)
Therefore `"DC"/"DA"="DA"/"DB"`
⇒AD2 = BD × CD
(iv) From part (i) 𝐴𝐵2 = 𝐶𝐵 × 𝐵𝐷
From part (ii) 𝐴𝐶2 = 𝐷𝐶 × 𝐵𝐶
Hence `"AB"^2/"AC"^2=(CBxxBD)/(DCxxBC)`
`"AB"^2/"AC"^2="BD"/"DC"`
Hence proved
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the sides of a triangle are 3 cm, 4 cm, and 6 cm long, determine whether the triangle is a right-angled triangle.
A ladder 17 m long reaches a window of a building 15 m above the ground. Find the distance of the foot of the ladder from the building.
A triangle has sides 5 cm, 12 cm and 13 cm. Find the length to one decimal place, of the perpendicular from the opposite vertex to the side whose length is 13 cm.
Calculate the height of an equilateral triangle each of whose sides measures 12 cm.
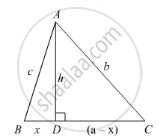
In the given figure, ∠B < 90° and segment AD ⊥ BC, show that
(i) b2 = h2 + a2 + x2 - 2ax
(ii) b2 = a2 + c2 - 2ax
If D, E, F are the respectively the midpoints of sides BC, CA and AB of ΔABC. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔDEF and ΔABC.
Find the diagonal of a rectangle whose length is 16 cm and area is 192 sq.cm ?
Find the side and perimeter of a square whose diagonal is `13sqrt2` cm.
From given figure, In ∆ABC, AB ⊥ BC, AB = BC then m∠A = ?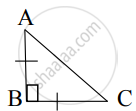
From given figure, In ∆ABC, AB ⊥ BC, AB = BC, AC = `5sqrt(2)` , then what is the height of ∆ABC?