Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Use polar co ordinates to evaluate `int int (x^2+y^2)^2/(x^2y^2)` 𝒅𝒙 𝒅𝒚 over yhe area Common to circle `x^2+y^2=ax "and" x^2+y^2=by, a>b>0`
Solution
Let I = `int int (x^2+y^2)^2/(x^2y^2)` 𝒅𝒙 𝒅𝒚
Region of integration is : Area common to the circle
`x^2+y^2=ax "and" x^2+y^2=by
To change the Cartesian coordinates to polar coordinates
Put x= r cos𝜽 and y = r sin 𝜽
Circles : r=acos 𝜽 𝒂𝒏𝒅 r=asin 𝜽
The function becomes : f(x,y) `= (x^2+y^2)^2/(x^2y^2)=r^4/(r^4sin^2thetacos^2theta)=4/(sin^2 2theta)=f(r,theta)`
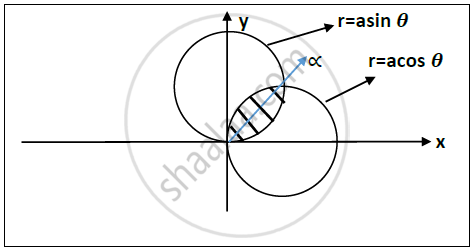
Intersection of both circles is at angle = `tan^(-1) a/b`
Divide the region into two equal halves.
For one region ,
𝟎≤𝒓≤𝒃𝒔𝒊𝒏𝜽
𝟎≤𝜽≤𝜶
For another region ,
𝟎≤𝒓≤𝒂𝒄𝒐𝒔 𝜽
𝜶≤𝜽≤`pi/2`
`therefore "I"=int_0^\alphaint_0^(bsintheta)(4rdrd theta)/(sin^2 2theta) + int_0^(acostheta) int_alpha^(pi/2)(4rdrd theta)/(sin^2 2theta)`
`therefore "I"=int_0^alpha 4/(sin^2 2theta)[r^2/2]_0^(bsin theta)d theta+int_0^(pi/2)4/(sin^2 2theta)[r^2/2]_0^(acostheta)d theta`
`=1/2b^2int_0^alphasec^2theta d theta+a^2/2int_alpha^(pi/2)cosec^2theta d theta`
`=1/2b^2tanalpha+a^2/2cotalpha`
`=(ab)/2+(ab)/2`
∴ I = ab
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the area inside the circle r=a sin𝜽 and outside the cardioide r=a(1+cos𝜽 )
Evaluate `int int xy(x-1)dx dy` over the region bounded by 𝒙𝒚 = 𝟒,𝒚= 𝟎,𝒙 =𝟏 and 𝒙 = 𝟒
Evaluate `int int(2xy^5)/sqrt(x^2y^2-y^4+1)dxdy`, where R is triangle whose vertices are (0,0),(1,1),(0,1).
Find by double integration the area bounded by the parabola 𝒚𝟐=𝟒𝒙 And 𝒚=𝟐𝒙−𝟒
