Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is Grignard reagent?
Solution
Grignard’s reagent is an organometallic compound in which the divalent magnesium is directly linked to an alkyl group acid and a halogen atom. It is represented by general formula R–Mg–X
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when \[\ce{CH3 - Br}\] is treated with KCN?
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Give two reasons for the same.
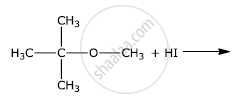
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
The presence of nitro group (−NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
Give reasons:
The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Write the product formed on reaction of D-glucose with Br2 water.
Write chemical equation in support of your answer.
Out of 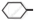 Cl and
Cl and 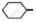 CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
Assertion: Presence of a nitro group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution.
Reason: Nitro group, being an electron-withdrawing group decreases the electron density over the benzene ring.
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by \[\ce{OH-}\] ion?
(a) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH - Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
(b) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
(c) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 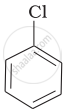 |
| (b) | 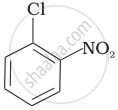 |
| (c) | 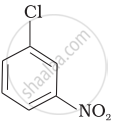 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 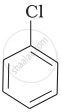 |
| (b) | 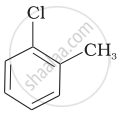 |
| (c) | 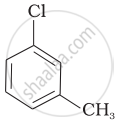 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 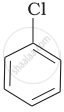 |
| (b) | 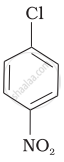 |
| (c) | 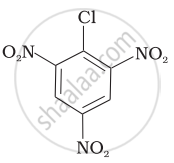 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 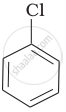 |
| (b) | 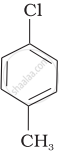 |
| (c) | 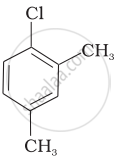 |
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain.
Allyl chloride is hydrolysed more readily than n-propyl chloride. Why?
\[\ce{C6H12O6 ->[(Zymase)] A ->[NaOH][\Delta] B + CHI3}\]
The number of carbon atoms present in the product B is:
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
Why haloarenes are not reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? Give two reactions.
