Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is a cell constant? What are its units? How is it determined experimentally?
Solution
For a given cell, the ratio of separation (l) between the two electrodes divided by the area of cross-section (a) of the electrode is called the cell constant.
Cell constant = `"l"/"a"`
The unit of cell constant is m-1 (SI unit) or cm-1 (C.G.S unit).
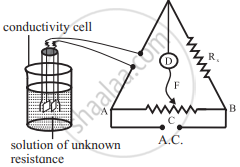
1) The cell constant is determined using the 1 M, 0.1 M or 0.01 M KCl solutions. The conductivity of KCl solution is well tabulated at various temperatures.
2) The resistance of KCl solution is measured by Wheatstone bridge as shown in the figure.
3) AB is the uniform wire. Rx is the variable known resistance placed in one arm of Wheatstone bridge. The conductivity cell containing KCl solution of unknown resistance is placed in the other arm of Wheatstone bridge.
4) D is a current detector. F is the sliding contact that moves along AB. A.C. represents the source of alternating current.
5) The sliding contact is moved along AB until no current flows. The detector D shows no deflection. The null point is, thus, obtained at C.
6) According to Wheatstone bridge principle,
`("R"_(("solution")))/(l("AC")) = "R"_"x"/(l("BC"))`
Hence, `"R"_(("solution")) = (l("AC"))/(l("BC")) xx "R"_"x"`
7) By measuring lengths AC and BC and knowing Rx , resistance of KCl solution can be calculated.
8) The cell constant is given by
Cell constant = kKCl × `"R"_(("solution"))`
The conductivity of KCl solution is known. The cell constant, thus, can be calculated.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the most correct option.
Two solutions have the ratio of their concentrations 0.4 and ratio of their conductivities 0.216. The ratio of their molar conductivities will be ______.
Write applications of Kohlrausch’s Law.
State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions.
Write three important steps required to determine molar conductivity.
Write relation between electrolytic conductivity and molar conductivity.
If resistivity of 0.8 M KCI solution is 2.5 × 10-3 Ω cm. Calculate molar conductivity of solution?
For the reaction \[\ce{A -> B}\], the rate increases by a factor of 2.25 when the concentration of A is increased by 1.5. What is the order of the reaction?
What will be the concentration of NaCl solution, if the molar conductivity and conductivity of NaCl solution is 124.3 Ω−1 cm2 mol−1 and 1.243 × 10−4 Ω−1 cm2 respectively?
The molar conductance of 0.001 M acetic acid is 50 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1. The limiting molar conductance is 250 ohm−1 cm2 mol−1. What is its degree of ionization?
The molar conductances at infinite dilution `(∧_0)` for electrolytes B+A− and C+A− are 140 and 120 S cm2 mol−1. The molar conductance at infinite dilution for B+X− is 198 S cm2 mol−1. The `∧_0` (in S cm2 mol−1) of C+X− is __________.
The conductivity of 0.02 M solution of NaCl is 2.6 × 10−2 S cm−1. What is its molar conductivity?
Which among the following solution has the highest conductivity (k) value?
Conductivity of KCI solution is 0.0027 Ω−1 m−1 at 25°C. The resistance of the solution is 82.4 Ω. The cell constant is ____________ m−1.
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing 0.001 M KCl solution at 298 K is 1500 Ω. What is the cell constant if conductivity of 0.001 M KCI solution at 298 K is 0.146 × 10−3 S cm−1?
What is the relation between cell constant, conductivity and electrical resistance?
The distance between electrodes of a conductivity cell is 0.98 cm and area of cross section is 1.96 cm2. What is the cell constant?
What is the unit of electrical conductance?
What will be the concentration of NaCl solution, if the molar conductivity and conductivity of NaCl solution is 124.3 Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 and 1.243 × 10-4 Ω-1 cm2 respectively?
If the conductivity of 0.08 M KCl solution is 2 × 10-2 Ω-1, what is the molar conductivity of the solution?
A conductivity cell dipped in 0.5 M KCl gives a resistance of 250 ohms. If the conductivity of KC I solution is 6.68 × 10-3 S cm-1, what is the cell constant?
What is the SI unit of conductivity?
What is the SI unit of molar conductivity?
