Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is an ideal gas?
Solution
An ideal or perfect gas is a gas which obeys the gas laws (Boyle’s law, Charles’ law and Gay-Lussac’s law) at all pressures and temperatures. An ideal gas cannot be liquefied by application of pressure or lowering the temperature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Determine the pressure of nitrogen at 0°C if the density of nitrogen at N.T.P. is 1.25 kg/m3 and R.M.S. speed of the molecules at N.T.P. is 489 m/s.
A sample of an ideal gas is at equilibrium. Which of the following quantity is zero?
If the internal energy of an ideal gas U and volume V are doubled then the pressure ____________.
The ratio γ = `"C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` for a gas mixture consisting of 8 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen is ____________.
Which of the following shows the correct relationship between the pressure and density of an ideal gas at constant temperature?
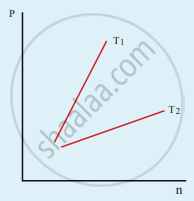
The following graph represents the pressure versus number density for an ideal gas at two different temperatures T1 and T2. The graph implies
What is the microscopic origin of pressure?
A gas is at temperature 80°C and pressure 5 × 10−10 Nm−2. What is the number of molecules per m3 if Boltzmann’s constant is 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1
If 1020 oxygen molecules per second strike 4 cm2 of wall at an angle of 30° with the normal when moving at a speed of 2 × 103 ms−1, find the pressure exerted on the wall. (mass of one oxygen atom = 2.67 × 10−26 kg)
Estimate the total number of air molecules in a room of a capacity of 25 m3 at a temperature of 27°C.
A perfect gas of 'N' molecules, each of mass 'm', moving with velocities 'C1', 'C2', ...... .'CN' is enclosed in a cubical vessel of volume 'V'. The pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the vessel is ______. ('p' = density of gas)
According to the assumptions made in the kinetic theory of gases, when two molecules of a gas collide with each other, then ______.
The average force applied on the walls of a closed container depends as 'Tx', where 'T' is the temperature of an ideal gas. The value of 'x' is ______.
Derive an expression for the pressure exerted by a gas on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Does an ideal gas exist in practice?
The kinetic energy per molecule of a gas at temperature T is ______.
Temperature remaining constant, if you double the number of molecules in a box, the pressure will ______.
The velocities of five molecules are 2 m/s, 3 m/s, 4 m/s, 5 m/s and 6 m/s. Find the root mean square velocity of molecules.
