Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer the following question.
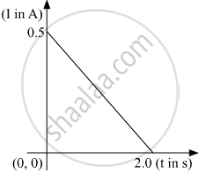
When a conducting loop of resistance 10 Ω and area 10 cm2 is removed from an external magnetic field acting normally, the variation of induced current-I in the loop with time t is as shown in the figure.
Find the
(a) total charge passed through the loop.
(b) change in magnetic flux through the loop
(c) magnitude of the field applied
Solution
`I = ("dq")/("dt") ⇒ "dq = "I"d"t"`
Hence area under the I-t curve gives charge flown.
Area of the I-t curve (as given in the question) = `1/2 xx 2 xx 1/2 = 0.5`
Total charge passed through the loop = 0.5 C
Now we know
`Δ"Q" = (Δvarphi)/"R"`
`Δvarphi = Δ"Q" xx "R" = 1/2 xx 10Omega = 5 "Wb"`
Charge in magnetic flux through the loop= 5 Wb
`Δvarphi = "B" (Δ"A")`
`5 = "B" (0.001)`
`"B" = 5000 "T"`
The magnitude of the field applied = 5000 T
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A square loop MNOP of side 20 cm is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field acting vertically downwards as shown in the figure. The loop is pulled with a constant velocity of 20 cm s−1 till it goes out of the field.
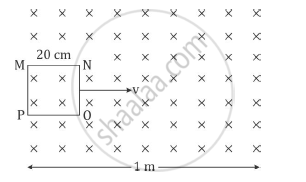
(i) Depict the direction of the induced current in the loop as it goes out of the field. For how long would the current in the loop persist?
(ii) Plot a graph showing the variation of magnetic flux and induced emf as a function of time.
A rectangular coil having 60 turns and area of 0.4m2 is held at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of flux density 5 × 10-5T. Calculate the magnetic flux passing through it.
How does the mutual inductance of a pair of coils change when
(i) distance between the coils is increased and
(ii) number of turns in the coils is increased?
Two inductors of inductance L each are connected in series with the opposite? magnetic fluxes. The resultant inductance is ______.
The dimensional formula of magnetic flux is ______.
A square of side L meters lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by `B = Bo(2hati + 3hatj + 4hatk)`T, where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square is ______.
A loop, made of straight edges has six corners at A(0, 0, 0), B(L, O, 0) C(L, L, 0), D(0, L, 0) E(0, L, L) and F(0, 0, L). A magnetic field `B = B_o(hati + hatk)`T is present in the region. The flux passing through the loop ABCDEFA (in that order) is ______.
A cylindrical bar magnet is rotated about its axis (Figure). A wire is connected from the axis and is made to touch the cylindrical surface through a contact. Then
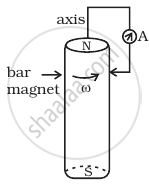
A circular coil of 1000 turns each with area 1 m2 is rotated about its vertical diameter at the rate of one revolution per second in a uniform horizontal magnetic field of 0.07T. The maximum voltage generation will be ______ V.
A circular coil has radius ‘r', number of turns ‘N’ and carries a current ‘I’. Magnetic flux density ‘B’ at its centre is ______.
