Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
When longitudinal wave is incident at the boundary of denser medium, then............................
- compression reflects as a compression.
- compression reflects as a rarefaction.
- rarefaction reflects as a compression.
- longitudinal wave reflects as transverse wave.
Solution
(a) compression reflects as a compression
A compression is reflected as a compression at the boundary of a denser medium, but it is reflected as a rarefaction at the boundary of a rarer medium.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When a transverse wave on a string is reflected from the free end, the phase change produced is ..............
(a) zero rad
(b) ` pi/2 ` rad
(c) `(3pi)/4` rad
(d) `pi` rad
A wire of density ‘ρ’ and Young’s modulus ‘Y’ is stretched between two rigid supports separated by a distance ‘L’ under tension ‘T’. Derive an expression for its frequency in fundamental mode. Hence show that `n=1/(2L)sqrt((Yl)/(rhoL))` where symbols have their usual meanings
A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
(b) What are its amplitude and frequency?
(c) What is the initial phase at the origin?
(d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = cos x sin t + cos 2x sin 2t
You are walking along a seashore and a mild wind is blowing. Is the motion of air a wave motion?
A transverse wave travels along the Z-axis. The particles of the medium must move
A wave going in a solid
(a) must be longitudinal
(b) may be longitudinal
(c) must be transverse
(d) may be transverse.
A wave moving in a gas
Mark out the correct options.
A particle on a stretched string supporting a travelling wave, takes 5⋅0 ms to move from its mean position to the extreme position. The distance between two consecutive particles, which are at their mean positions, is 2⋅0 cm. Find the frequency, the wavelength and the wave speed.
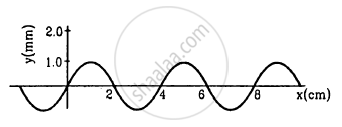
Figure shows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cm s−1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.
A vertical rod is hit at one end. What kind of wave propagates in the rod if (a) the hit is made vertically (b) the hit is made horizontally?
Two wires of different densities but same area of cross section are soldered together at one end and are stretched to a tension T. The velocity of a transverse wave in the first wire is double of that in the second wire. Find the ratio of the density of the first wire to that of the second wire.
A transverse wave described by \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 02 m \right) \sin \left( 1 \cdot 0 m^{- 1} \right) x + \left( 30 s^{- 1} \right)t\] propagates on a stretched string having a linear mass density of \[1 \cdot 2 \times {10}^{- 4} kg m^{- 1}\] the tension in the string.
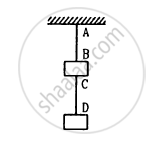
Two blocks each having a mass of 3⋅2 kg are connected by a wire CD and the system is suspended from the ceiling by another wire AB (See following figure). The linear mass density of the wire AB is 10 g m−1 and that of CD is 8 g m−1. Find the speed of a transverse wave pulse produced in AB and CD.
An organ pipe, open at both ends, contains
A circular loop of string rotates about its axis on a frictionless horizontal place at a uniform rate so that the tangential speed of any particle of the string is ν. If a small transverse disturbance is produced at a point of the loop, with what speed (relative to the string) will this disturbance travel on the string?
A transverse wave of amplitude 0⋅50 mm and frequency 100 Hz is produced on a wire stretched to a tension of 100 N. If the wave speed is 100 m s−1, what average power is the source transmitting to the wire?
A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz is attached to a long string of linear mass density 0⋅01 kg m−1 kept under a tension of 49 N. The fork produces transverse waves of amplitude 0⋅50 mm on the string. (a) Find the wave speed and the wavelength of the waves. (b) Find the maximum speed and acceleration of a particle of the string. (c) At what average rate is the tuning fork transmitting energy to the string?
If the speed of a transverse wave on a stretched string of length 1 m is 60 m−1, what is the fundamental frequency of vibration?
A steel wire of mass 4⋅0 g and length 80 cm is fixed at the two ends. The tension in the wire is 50 N. Find the frequency and wavelength of the fourth harmonic of the fundamental.
A wire, fixed at both ends is seen to vibrate at a resonant frequency of 240 Hz and also at 320 Hz. (a) What could be the maximum value of the fundamental frequency? (b) If transverse waves can travel on this string at a speed of 40 m s−1, what is its length?
The equation of a standing wave, produced on a string fixed at both ends, is
\[y = \left( 0 \cdot 4 cm \right) \sin \left[ \left( 0 \cdot 314 {cm}^{- 1} \right) x \right] \cos \left[ \left( 600\pi s^{- 1} \right) t \right]\]
What could be the smallest length of the string?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 2 cos (3x) sin (10t)
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 3 sin (5x – 0.5t) + 4 cos (5x – 0.5t)
