Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
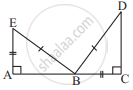
Which congruence criterion do you use in the following?
Given: EB = DB
AE = BC
∠A = ∠C = 90°
So, ΔABE ≅ ΔCDB
Solution
RHS, as in the given two right-angled triangles, one side and the hypotenuse are respectively equal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
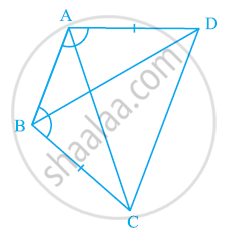
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and ∠DAB = ∠CBA (See the given figure). Prove that
- ΔABD ≅ ΔBAC
- BD = AC
- ∠ABD = ∠BAC.
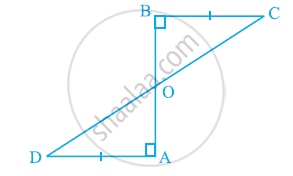
AD and BC are equal perpendiculars to a line segment AB (See the given figure). Show that CD bisects AB.
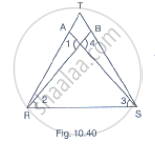
In Fig. 10.40, it is given that RT = TS, ∠1 = 2∠2 and ∠4 = 2∠3. Prove that ΔRBT ≅ ΔSAT.
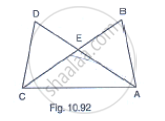
In Fig. 10.92, it is given that AB = CD and AD = BC. Prove that ΔADC ≅ ΔCBA.
If perpendiculars from any point within an angle on its arms are congruent, prove that it lies on the bisector of that angle.
Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F):
If any two sides of a right triangle are respectively equal to two sides of other right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
If the following pair of the triangle is congruent? state the condition of congruency:
In ΔABC and ΔPQR, AB = PQ, AC = PR, and BC = QR.
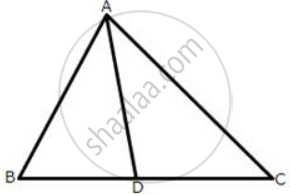
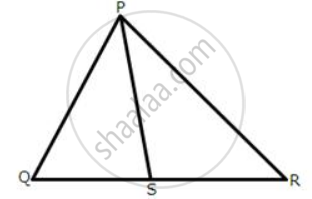
In the following figures, the sides AB and BC and the median AD of triangle ABC are equal to the sides PQ and QR and median PS of the triangle PQR.
Prove that ΔABC and ΔPQR are congruent.
 |
 |
In the following diagram, ABCD is a square and APB is an equilateral triangle.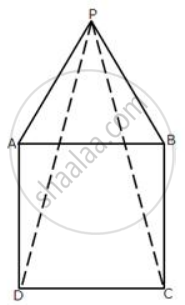
(i) Prove that: ΔAPD ≅ ΔBPC
(ii) Find the angles of ΔDPC.
In the following diagram, AP and BQ are equal and parallel to each other. 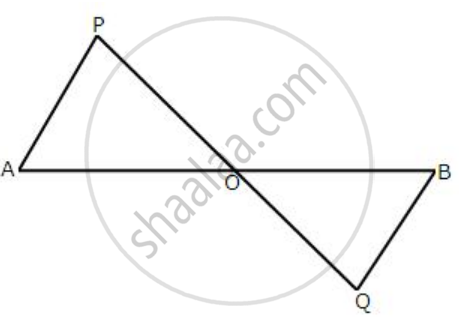
Prove that: AB and PQ bisect each other.
