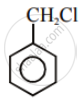
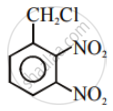
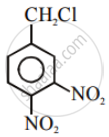
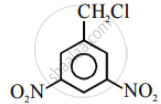
Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Out of 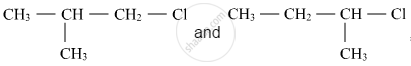 , which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
, which is more reactive towards SN1 reaction and why?
Solution
Since formation of carbocation is the rate-determining step in the SN1 reaction, the stability of carbocation would determine its reactivity.
The order of stability of carbocation is as follows:
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary >Methyl
Here, 1-chloro-1-methylpropane would form secondary carbocation, while 1-chloro-2-methylpropane will form primary carbocation, which is less stable than secondary carbocation. Hence, reactivity towards the SN1 reaction would be higher for 1-chloro-1-methylpropane.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
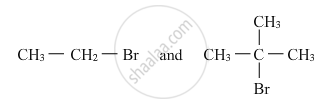
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
What happens when methyl chloride is treated with KCN?
SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
The order of reactivity of the given haloalkanes towards nucleophile is:
Which of the following is a chiral compound?
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
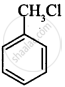
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is ______.
Convert bromoethane to propanamine.