Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does a phonograph record attract dust particles just after it is cleaned?
Solution
When a phonograph record is cleaned, it develops a charge on its surface due to rubbing. This charge attracts the neutral dust particles due to induction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
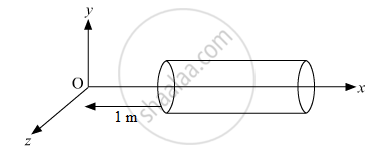
A hollow cylindrical box of length 1 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 50xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
Can a gravitational field be added vectorially to an electric field to get a total field?
A point charge q is rotated along a circle in an electric field generated by another point charge Q. The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
The electric field and the electric potential at a point are E and V, respectively.
Which of the following quantities does not depend on the choice of zero potential or zero potential energy?
A particle of mass m and charge q is thrown at a speed u against a uniform electric field E. How much distance will it travel before coming to momentary rest ?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. Find the electric force and the force of gravity acting on this particle. Can one of these forces be neglected in comparison with the other for approximate analysis?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How long will it take for the particle to travel a distance of 40 cm?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. How much is the work done by the electric force on the particle during this period?
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 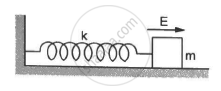
12 J of work has to be done against an existing electric field to take a charge of 0.01 C from A to B. How much is the potential difference VB − VA?
An electric field \[\vec{E} = \vec{i}\] Ax exists in space, where A = 10 V m−2. Take the potential at (10 m, 20 m) to be zero. Find the potential at the origin.
Find the magnitude of the electric field at the point P in the configuration shown in the figure for d >> a.
The surface charge density of a thin charged disc of radius R is σ. The value of the electric field at the center of the disc is `sigma/(2∈_0)`. With respect to the field at the center, the electric field along the axis at a distance R from the center of the disc ______.
Consider a region inside which, there are various types of charges but the total charge is zero. At points outside the region ______.
When 1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes ______.
Five charges, q each are placed at the corners of a regular pentagon of side ‘a’ (Figure).
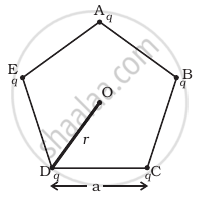
(a) (i) What will be the electric field at O, the centre of the pentagon?
(ii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge from one of the corners (say A) is removed?
(iii) What will be the electric field at O if the charge q at A is replaced by –q?
(b) How would your answer to (a) be affected if pentagon is replaced by n-sided regular polygon with charge q at each of its corners?
