Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following quantities does not depend on the choice of zero potential or zero potential energy?
Options
Potential at a point
Potential difference between two points
Potential energy of a two-charge system
None of these
Solution
Potential difference between two points
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?

Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
Consider a system of n charges q1, q2, ... qn with position vectors `vecr_1,vecr_2,vecr_3,...... vecr_n`relative to some origin 'O'. Deduce the expression for the net electric field`vec E` at a point P with position vector `vecr_p,`due to this system of charges.
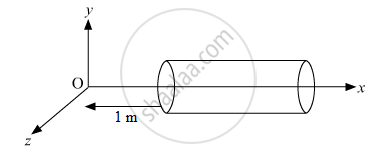
A hollow cylindrical box of length 0.5 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 20 xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
When the separation between two charges is increased, the electric potential energy of the charges
The electric field at the origin is along the positive x-axis. A small circle is drawn with the centre at the origin, cutting the axes at points A, B, C and D with coordinates (a, 0), (0, a), (−a, 0), (0, −a), respectively. Out of the points on the periphery of the circle, the potential is minimum at
If a body is charged by rubbing it, its weight
The electric field and the electric potential at a point are E and V, respectively.
A wire is bent in the form of a regular hexagon and a total charge q is distributed uniformly on it. What is the electric field at the centre? You may answer this part without making any numerical calculations.
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 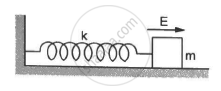
An electric field of 20 NC−1 exists along the x-axis in space. Calculate the potential difference VB − VA where the points A and B are
(a) A = (0, 0); B = (4 m, 2m)
(b) A = (4 m, 2 m); B = (6 m, 5 m)
(c) A = (0, 0); B = (6 m, 5 m)
Do you find any relation between the answers of parts (a), (b) and (c)?
An electric field \[\vec{E} = \vec{i}\] Ax exists in space, where A = 10 V m−2. Take the potential at (10 m, 20 m) to be zero. Find the potential at the origin.
The electric potential existing in space is \[\hspace{0.167em} V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx) .\] (a) Write the dimensional formula of A. (b) Find the expression for the electric field. (c) If A is 10 SI units, find the magnitude of the electric field at (1 m, 1 m, 1 m).
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
Assume that each atom in a copper wire contributes one free electron. Estimate the number of free electrons in a copper wire of mass 6.4 g (take the atomic weight of copper to be 64 g mol−1).
Two identical blocks are kept on a frictionless horizontal table connected by a spring of stiffness k and of original length l0. A total charge Q is distributed on the block such that maximum elongation of spring at equilibrium is equal to x. Value of Q is ______.
When 1014 electrons are removed from a neutral metal sphere, the charge on the sphere becomes ______.
