Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The electric potential existing in space is \[\hspace{0.167em} V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx) .\] (a) Write the dimensional formula of A. (b) Find the expression for the electric field. (c) If A is 10 SI units, find the magnitude of the electric field at (1 m, 1 m, 1 m).
Solution
Given:
Electric potential,
\[V(x, y, z) = A(xy + yz + zx)\]
\[A = \frac{\text{ volt }}{m^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left[ A \right] = \frac{\left[ {ML}^2 I^{- 1} T^{- 3} \right]}{\left[ L^2 \right]}\]
\[ \Rightarrow A = [ {MT}^{- 3} I^{- 1} ]\]
(b) Let E be the electric field.
\[dV = - \vec{E} . \vec{dr} \]
\[ \Rightarrow A(y + z)dx + A(z + x)dy + A(x + y)dz = - E(dx \hat{i} + dy \hat{j} + dz\hat{ k } )\]
\[ \Rightarrow [A(y + z) \hat{i } + A(z + x)\hat{ j } + A(x + y) \hat{ k } ] [dx\hat{ i} + dy \hat{j } + dz \hat{k } ] = - E\left[ dx \hat{ i }+ dy\hat{ j } + dz \hat{ k } \right]\]
Equating now, we get
\[\vec{E} = - A(y + z) \hat{ i } - A(z + x) \hat{ j } - A(x + y) \hat{ k }\]
(c) Given: A = 10 V/m2
\[r = (1 m, 1 m, 1 m)\]
\[ \vec{E} = - 10 (2) \hat{ i } - 10 (2) \hat{ j } - 10 (2) \hat{ k } \]
\[ = - 20 \hat{ i } - 20 \hat{ j } - 20 \hat{ k }\]
Magnitude of electric field,
\[\left| E \right| = \sqrt{{20}^2 + {20}^2 + {20}^2}\]
\[ = \sqrt{1200} = 34 . 64 = 35\] N/C
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The figure shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?

Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
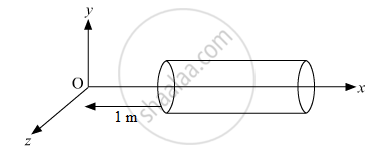
A hollow cylindrical box of length 1 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 50xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
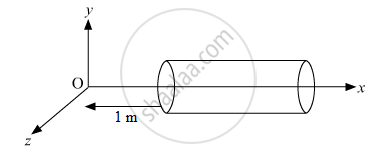
A hollow cylindrical box of length 0.5 m and area of cross-section 25 cm2 is placed in a three dimensional coordinate system as shown in the figure. The electric field in the region is given by `vecE = 20 xhati` where E is NC−1 and x is in metres. Find
(i) Net flux through the cylinder.
(ii) Charge enclosed by the cylinder.
Can a gravitational field be added vectorially to an electric field to get a total field?
Why does a phonograph record attract dust particles just after it is cleaned?
In some old texts it is mentioned that 4π lines of force originate from each unit positive charge. Comment on the statement in view of the fact that 4π is not an integer.
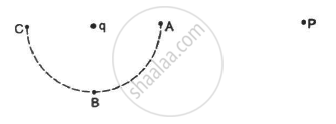
Consider the situation in the figure. The work done in taking a point charge from P to Ais WA, from P to B is WB and from P to C is WC.
A 10-cm long rod carries a charge of +50 μC distributed uniformly along its length. Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 10 cm from both ends of the rod.
A particle of mass 1 g and charge 2.5 × 10−4 C is released from rest in an electric field of 1.2 × 10 4 N C−1. What will be the speed of the particle after travelling this distance?
A block of mass m with a charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is connected to a wall through an unstressed spring of spring constant k, as shown in the figure. A horizontal electric field E, parallel to the spring, is switched on. Find the amplitude of the resulting SHM of the block. 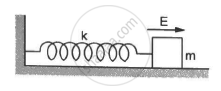
The kinetic energy of a charged particle decreases by 10 J as it moves from a point at potential 100 V to a point at potential 200 V. Find the charge on the particle.
Find the magnitude of the electric field at the point P in the configuration shown in the figure for d >> a.
Assume that each atom in a copper wire contributes one free electron. Estimate the number of free electrons in a copper wire of mass 6.4 g (take the atomic weight of copper to be 64 g mol−1).
Which of the following methods can be used to charge a metal sphere positively without touching it? Select the most appropriate.
The Electric field at a point is ______.
- always continuous.
- continuous if there is no charge at that point.
- discontinuous only if there is a negative charge at that point.
- discontinuous if there is a charge at that point.
