Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2014-2015
Date: March 2015
Advertisements
The line AB in the ray diagram represents a lens State whether the lens is convex or concave.
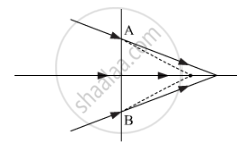
Chapter:
Distinguish between emf and terminal voltage of a cell.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw a graph to show variation of capacitive-reactance with frequency in an a.c. circuit.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
What is the function of a 'Repeater' used in communication system?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
The field lines of a negative point charge are as shown in the figure. Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from B to A?
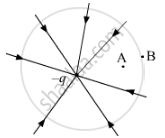
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
The equivalent wavelength of a moving electron has the same value as that of a photon of energy 6 × 10–17 J. Calculate the momentum of the electron.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
What is ground wave communication?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Explain why this mode cannot be used for long distance communication using high frequencies.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A ray of light passes through an equilateral glass prism such that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and each of these angles is equal to 3/4 of angle of prism. Find the angle of deviation.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 45°. Does critical angle for a given pair of media depend on the wavelength of incident light ? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
How does one explain, using de Broglie hypothesis, Bohr's second postulate of quantization of orbital angular momentum?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
In a meter bridge shown in the figure, the balance point is found to be 40 cm from end A. If a resistance of 10 Ω is connected in series with R, balance point is obtained 60 cm from A. Calculate the values of R and S.
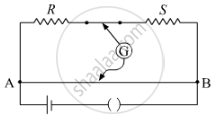
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
In a given coil of self-inductance of 5 mH, current changes from 4 A to 1 A in 30 ms. Calculate the emf induced in the coil.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
In what way is Gauss's law in magnetism different from that used in electrostatics ? Explain briefly.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
The Earth's magnetic field at the Equator is approximately 0.4 G. Estimate the Earth's magnetic dipole moment. Given : Radius of the Earth = 6400 km.
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
What is the source of energy of electromagnetic waves?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Draw a schematic sketch of the electromagnetic waves propagating along the + x-axis. Indicate the directions of the electric and magnetic fields
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Write the relation between the velocity of propagation and the magnitudes of electric and magnetic fields.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Obtain the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive sample.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
The half life of a certain radioactive material against \u0003α-decay is 100 days. After how much time, will the undecayed fraction of the material be 6.25%?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Advertisements
How is a Zener diode fabricated?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the principle and working of a Zener diode as voltage regular.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Find the equivalent capacitance of the network shown in the figure, when each capacitor is of 1 μF. When the ends X and Y are connected to a 6 V battery, find out (i) the charge and (ii) the energy stored in the network.
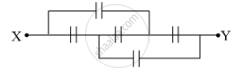
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
State the underlying principle of a potentiometer ?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Write two factors by which current sensitivity of a potentiometer can be increased.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
On what factors does the potential gradient of the wire depend?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Define the term 'intensity of radiation' in terms of photon picture of light.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Two monochromatic beams, one red and the other blue, have the same intensity. In which case (i) the number of photons per unit area per second is larger, (ii) the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is more? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
a) Give two reasons to explain why reflecting telescopes are preferred over refracting type.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Use the mirror equation to show that a convex mirror always produces a virtual image independent of the location of the object.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write the necessary conditions to obtain sustained interference fringes.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
In Young's double slit experiment, plot a graph showing the variation of fringe width versus the distance of the screen from the plane of the slits keeping other parameters same. What information can one obtain from the slope of the curve?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
What is the effect on the fringe width if the distance between the slits is reduced keeping other parameters same?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A series LCR circuit is connected across an a.c. source of variable angular frequency 'ω'. Plot a graph showing variation of current 'i' as a function of 'ω' for two resistances R1 and R2 (R1 > R2).
Answer the following questions using this graph :
(a) In which case is the resonance sharper and why?
(b) In which case in the power dissipation more and why?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Draw the necessary energy band diagrams to distinguish between conductors, semiconductors and insulators.
How does the change in temperature affect the behaviour of these materials ? Explain briefly.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
What are the three basic units in communication systems ? Write briefly the function of each of these.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Advertisements
Write any three applications of the Internet used in communication systems.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
During a thunderstorm the 'live' wire of the transmission line fell down on the ground from the poles in the street. A group of boys, who passed through, noticed it and some of them wanted to place the wire by the side. As they were approaching the wire and trying to lift the cable, Anuj noticed it and immediately pushed them away, thus preventing them from touching the live wire. During pushing some of them got hurt. Anuj took them to a doctor to get them medical aid.
Based on the above paragraph, answer the following questions :
(a) Write the two values which Anuj displayed during the incident.
(b) Why is it that a bird can sit on a suspended 'live' wire without any harm whereas touching it on the ground can give a fatal shock ?
(c) The electric power from a power plant is set up to a very high voltage before transmitting it to distant consumers. Explain, why.
Chapter:
Use Huygens' principle to show the propagation of a plane wavefront from a denser medium to a rarer medium. Hence find the ratio of the speeds of wavefronts in the two media.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Why does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get linearly polarised ?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Derive the expression of Brewster's law when unpolarised light passing from a rarer to a denser medium gets polarised on reflection at the inteface.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
A biconvex lens with its two faces of equal radius of curvature R is made of a transparent medium of refractive index μ1. It is kept in contact with a medium of refractive index μ2 as shown in the figure.
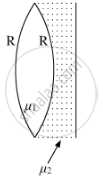
(a) Find the equivalent focal length of the combination.
(b) Obtain the condition when this combination acts as a diverging lens.
(c) Draw the ray diagram for the case μ1 > (μ2 + 1) / 2, when the object is kept far away from the lens. Point out the nature of the image formed by the system.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Two infinitely long straight parallel wires, '1' and '2', carrying steady currents I1 and I2 in the same direction are separated by a distance d. Obtain the expression for the magnetic field `vecB`due to the wire '1' acting on wire '2'. Hence find out, with the help of a suitable diagram, the magnitude and direction of this force per unit length on wire '2' due to wire '1'. How does the nature of this force changes if the currents are in opposite direction? Use this expression to define the S.I. unit of current.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Draw a necessary arrangement for winding of primary and secondary coils in a step-up transformer. State its underlying principle and derive the relation between the primary and secondary voltages in terms of number of primary and secondary turns. Mention the two basic assumptions used in obtaining the above relation.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
State any two causes of energy loss in actual transformers.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
State Kirchhoff's rules and explain on what basis they are justified.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Two cells of emf E1 and E2 and internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in parallel. Derive the expression for the (i) emf and (ii) internal resistance of a single equivalent cell which can replace this combination.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
"The outward electric flux due to charge +Q is independent of the shape and size of the surface which encloses is." Give two reasons to justify this statement.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Two identical circular loops 1 and 2 of radius R each have linear charge densities −λ and +λ C/m respectively. The loops are placed coaxially with their centres `Rsqrt3` distance apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the centre of loop 1.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2014 - 2015
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2015 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
