(English Medium)
Academic Year: 2016-2017
Date & Time: 26th March 2017, 1:00 pm
Duration: 2h
Advertisements
Question 1 to Question 4 is compulsory
Attempt any four questions from Question 5 to Question 10.
A brass ball is hanging from a stiff cotton thread. Draw a neat labeled diagram showing the forces acting on the brass ball and cotton thread
Chapter: [0.01] Force
The distance between two bodies is doubled. How is the magnitude of the gravitational force between them affected?
Chapter: [0.01] Force
Why is a jack screw provided with a long arm?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
If the power of a motor is 100 kW, at what speed can it raise a load of 50,000 N?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Which class of lever will always have MA > 1 and why?
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
Define heat capacity and state its SI unit.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
Why is the base of a cooking pan generally made thick?
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
A solid of mass 50 g at 150 °C is placed in 100 g of water at 11 °C when the final temperature recorded is 20 °C. Find the specific heat capacity of the solid. (specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g °C)
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
How is the refractive index of a material related to real and apparent depth?
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
How is the refractive index of a material related to the velocity of light in vacuum or air and the velocity of light in a given medium?
Chapter:
State the conditions required for total internal reflection of light to take place
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic ray through a prism when it suffers minimum deviation
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
The human ear can detect continuous sounds in the frequency range from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Assuming that the speed of sound in air is 330 ms1 for all frequencies; calculate the wavelengths corresponding to the given extreme frequencies of the audible range
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
An enemy plane is at a distance of 300 km from a radar. In how much time the radar will be able to detect the plane? Take velocity of radio waves as 3 x 108 ms-1
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Advertisements
How is the frequency of a stretched string related to its length?
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
How is the frequency of a stretched string related it’s tension?
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Define specific resistance.
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
An electric bulb of 300Ω draws a current of 0.4 A. Calculate the power of the bulb and the potential difference at its ends.
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
State two causes of energy loss in a transformer.
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
State two characteristics of a good thermion emitter.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry [0.11] Calorimetry
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry [0.11] Calorimetry
When does the nucleus of an atom tend to become radioactive?
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
A uniform half meter rule balances horizontally on a knife-edge at 29 cm mark when a weight of 20 gf is suspended from one end
1) Draw a diagram of the arrangement
2) What is the weight of the half meter rule?
Chapter: [0.01] Force
A boy uses a single fixed pulley to lift a load of 50 kgf to some height. Another boy uses a single movable pulley to lift the same load to the same height. Compare the effort applied by them. Give a reason to support your answer.
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
How does uniform circular motion differ from uniform linear motion?
Chapter: [0.01] Force
Name the process used for producing electricity using nuclear energy.
Chapter:
A pulley system with VR = 4 is used to lift a load of 175 kgf through a vertical height of 15 m. The effort required is 50 kgf in the downward direction.
(g = 10 N kg-1)
Calculate
1) Distance moved by the effort
2) Work done by the effort
3) M.A. of the pulley system
4) Efficiency of the pulley system
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
How is the transference of heat energy by radiation prevented in a calorimeter?
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
You have a choice of three metals A, B, and C, of specific heat capacities 900 Jkg-1 °C-1, 380 Jkg-1 °C-1 and 460 Jkg-1 °C-1 respectively, to make a calorimeter. Which material will you select? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
Calculate the mass of ice needed to cool 150 g of water contained in a calorimeter of mass 50 g at 32 °C such that the final temperature is 5 °C. Specific heat capacity of calorimeter = 0.4 J g-1 °C-1, Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1°C-1, latent heat capacity of ice = 330 J g-1.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
Name the radiations which are absorbed by greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere.
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
A radiation X is focused by a particular device on the bulb of a thermometer and mercury in the thermometer shows a rapid increase. Name the radiation X
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Name two factors on which the heat energy liberated a body depend.
Chapter:
Advertisements
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object when the object is placed at its focal point. Name the lens and draw a ray diagram to show the image formation.
Chapter: [0.05] Refraction Through a Lense
A ray of light travels from water to air as shown in the diagram given below :

1) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the way. Given the critical angle for water is 48°.
2) State the condition so that internal reflection occurs in the above diagram.
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
The diagram below shows a point source P inside a water container. Four rays A, B, C, D starting from the source P are shown up to the water surface
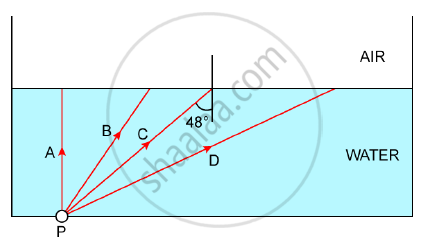
1) Show in the diagram the path of these rays after striking the water surface.
The Critical Angle for the water-air surface is 48°.
2) Name the phenomenon which the rays B and D exhibit.
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Name the factor that determines Loudness of the sound heard.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Name the factor that determines Quality of the note
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Name the factor that determines Pitch of the note.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Give one example of damped vibrations
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Name the phenomenon that causes a loud sound when the stem of a vibrating tuning fork is kept pressed on the surface of a table.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
A wire of length 80 cm has a frequency of 256 Hz. Calculate the length of a similar wire under similar tension, which will have frequency 1024 Hz
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
A certain sound has a frequency of 256 hertz and a wavelength of 1.3 m.
1) Calculate the speed with which this sound travels
2) What difference would be felt by a listener between the above sound and another sound traveling at the same speed, but of wavelength 2.6 m?
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Name the color code of the wire which is connected to the metallic body of an appliance.
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
Draw the diagram of a dual control switch when the appliance is switched ‘ON’.
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
Which particles are responsible for current in conductors?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
To which wire of a cable in a power circuit should the metal case of geyser be connected.
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
To which wire should the fuse be connected?
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
Explain the meaning of the student 'current rating of a fuse is 5A'.
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
In the transmission of power the voltage of power generated at the generating stations is stepped up from 11kV to 132 kV before it is transmitted. Why?
Chapter: [0.09] Household Circuits
Answer the following questions based on a hot cathode ray tube
Name the charged particles
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Answer the following questions based on a hot cathode ray tube.
State the approximate voltage used to heat the filament
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Answer the following questions based on a hot cathode ray tube.
What will happen to the beam when it passes through the electric field?
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
State three factors on which the rate of emission of electrons from a metal surface depends
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Why do Free electrons not leave the metal surface on their own
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
How can they be made to leave the metal surface? (State any two ways)
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers ICSE Class 10 Physics with solutions 2016 - 2017
Previous year Question paper for CISCE ICSE Class 10 -2017 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE ICSE Class 10 .
How CISCE ICSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
