ISC (Commerce)
ISC (Arts)
ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2017-2018
Date: March 2018
Advertisements
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from the brackets
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74; 26, sp3d2, sp3d, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas)
A Galvanic cell converts _______ energy into _______ energy.
Chapter: [0.062] Galvanic cells, mechanism of current production in a galvanic cell;
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from the brackets
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74; 26, sp3d2, sp3d, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas)
The percentage of unoccupied spaces in bcc and fcc arrangements are _______ and _____respectively
Chapter: [0.02] States of Matters: Structure and Properties Solid State
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from the brackets
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74; 26, sp3d2, sp3d, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas)
Propane-2-ol on reaction with iodine and sodium hydroxide gives ________ precipitate and the
reaction is called ___________ test.
Chapter: [0.115] Preparation, properties, and uses of the following
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from the brackets
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74; 26, sp3d2, sp3d, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas)
The geometry of XeOF4 molecule is ______ and the hybridisation of Xenon atom in the molecule is ________.
Chapter: [0.08] Chemistry of p-Block Elements: Group 16, 17, 18
During the course of an SN1 reaction, the intermediate species formed is:
(1) a carbocation
(2) a free radical
(3) a carbanion
(4) an intermediate complex
Chapter:
Purification of aluminium by electrolytic refining is carried out by
(a)Hoope process
(b)Hall process
(c)Baeyer process
(d)Serperck process
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
An aqueous solution of urea freezes at – 0.186°C, Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mo1–1, Kb for water = 0.512 K kg mo1–1. The boiling point of urea solution will be:
373.065 K
373.186 K
373.512 K
373.0512 K
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
In the dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with concentrated sulphuric acid, the initiation step is:
(1) formation of carbonation
(2) formation of an ester
(3) protonation of the alcohol molecule
(4) elimination of water
Chapter: [0.124] Classification, general formulae, structure and nomenclature [0.132] Ethers
Match the following
| 1 | Rate constant | a | Dialysis |
| 2 | Biodegradable polymer | b | Glycine |
| 3 | Zwitterion | c | Arrhenius equation |
| 4 | Purification of colloids | d | PHBV |
Chapter: [0.015] Normality, molality
Why does the density of transition elements increase from Titanium to Copper? (at. no. Ti = 22,
Cu = 29)
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Account for the following :
Zn is not considered as a transition element.
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Identify the compounds A, B, C and D.
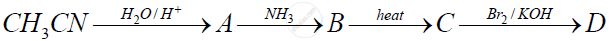
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Calculate the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 0.025 g of K2SO4 in 2.0 litres of water at 25°C assuming that K2SO4 is completely dissociated. (Mol. wt. of K2SO4 = 174 g mol–1)
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
What type of isomerism is shown by the following coordination compounds
`[PtCl_2(NH_3)_4]Br_2 and [PtBr_2(NH_3)_4]Cl_2`
Write their IUPAC names.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Write the rate law expression for the reaction A+B+C→D+E, if the order of reaction is first, second and zero with respect to A, B and C, respectively.
Chapter: [0.030299999999999997] Mechanism of the reaction
How many times the rate of reaction will increase if the concentration of A, B and C are doubled in the equation given in (i) above?
Chapter: [0.030299999999999997] Mechanism of the reaction
The rate of a reaction quadruples when the temperature changes from 293 K to 313 K. Calculate the energy of activation of the reaction assuming that it does not change with temperature.
Chapter: [0.0305] The concept of energy
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants? Give one example of each.
Chapter: [0.18] Chemistry in Everyday Life
State the role of the following chemicals in the food industry:
(i) Sodium benzoate
(ii) Aspartame
Chapter: [0.09] Preparation/ Manufacture, Properties and Uses of Compounds of Groups 16, 17, – Ozone, Sulphur Dioxide, Sulphuric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid
An aromatic organic compound [A] on heating with NH3 and Cu2O at high pressure gives [B]. The compound [B] on treatment with the ice-cold solution of NaNO2 and HCI gives [C], which on heating with Cu/HCl gives compound [A] again. Identify the compounds [A], [B] and [C]. Write the name of the reaction for the conversion of [B] to [C].
Chapter: [0.15] Cyanides, Isocyanides, Nitro compounds, Amines and Diazonium Salt
Advertisements
Write the name of the monomer of the following polymer:
Bakelite
Chapter: [0.16] Polymers
Write the name of the monomer of the following polymer:
Nylon – 2 – Nylon – 6
Chapter: [0.16] Polymers
Name the purine bases and pyrimidine bases present in RNA and DNA.
Chapter: [0.17] Biomolecules – carbohydrates, proteins, enzymes, vitamins and nucleic acids
How will you obtain the following? (Give balanced equation.)
Picric acid from phenol.
Chapter: [0.12300000000000001] Distinction between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
How will you obtain the following? (Give balanced equation.)
Ethyl chloride from diethyl ether.
Chapter: [0.132] Ethers
How will you obtain the following? (Give balanced equation.)
(i) Anisole from phenol
(ii) Ethyl acetate from ethanol.
Chapter: [0.12300000000000001] Distinction between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
40% of a first-order reaction is completed in 50 minutes. How much time will it take for the completion of 80% of this reaction?
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
The freezing point of a solution containing 5.85 g of NaCl in 100 g of water is -3.348°C. Calculate Van’t Hoff factor ‘i’ for this solution. What will be the experimental molecular weight of NaCl?
(Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol-1, at. wt. Na = 23, Cl = 35.5)
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
Examine the defective crystal given below and answer the question that follows:
| A+ | B- | A+ | B- | A+ |
| B- | B- | A+ | B- | |
| A+ | B- | A+ | A+ | |
| B- | A+ | B- | A+ | B- |
State if the above defect is stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric. How does this defect affect the density of the crystal? Also, write the term used for this type of defect.
Chapter: [0.02] States of Matters: Structure and Properties Solid State
Give a Reason for the Following:
For Ferric Hydroxide Sol. the Coagulating Power of Phosphate Ion is More than Chloride Ion.
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
Give the reason for the following:
Medicines are more effective in their colloidal form.
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
Give the reason for the following:
Gelatin is added to ice creams.
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
For the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3- state:
(i) the type of hybridisation.
(ii) the magnetic behaviour.
(iii) the oxidation number of the central metal atom.
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Write the IUPAC name of [Co(en)2Cl2]+ ion and draw the structures of its geometrical isomers.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Explain why:
(i) Mn2+ is more stable than Fe2+ towards oxidation to +3 state.
(At. no. of Mn = 25, Fe = 26)
(ii) Transition elements usually form coloured ions.
(iii) Zr and Hf exhibit similar properties.
(At. no. of Zr = 40, Hf = 72)
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Complete and balance the following chemical equation:
\[\ce{KMnO4 + KI + H2SO4 → }\]_____ + _____ + _____ + ______
Chapter: [0.121] Methods of preparation, manufacture, properties and use
Complete and balance the following chemical equation:
\[\ce{K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 + H2S →}\]____ + ____ + ____ + ____
Chapter: [0.121] Methods of preparation, manufacture, properties and use
Complete and balance the following chemical equation:
\[\ce{KMnO4 + H2SO4 + FeSO4 →}\] _____ + _____ + _____ + ____
Chapter: [0.121] Methods of preparation, manufacture, properties and use
Advertisements
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their basic strength:
Chapter: [0.15] Cyanides, Isocyanides, Nitro compounds, Amines and Diazonium Salt
Give a balanced chemical equation to convert methyl cyanide to ethyl alcohol.
Chapter: [0.114] Chlorobenzene
What happens when benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in the weak alkaline medium?
(Give a balanced equation).
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Name the sulphide ore of Copper. Describe how pure copper is extracted from this ore.
Chapter: [0.08] Chemistry of p-Block Elements: Group 16, 17, 18
Calculate the emf and ΔG° for the cell reaction at 25°C:
\begin{array}{cl}{\mathrm{Zn}(s) | \mathrm{Zn}_{(a q)}^{2+} \|} & {\mathrm{Cd}_{(a q)}^{2+} | \mathrm{Cd}_{(s)}} \\ \ce{(0 \cdot 1 \mathrm{M})} & \ce{(0 \cdot 01 \mathrm{M})}\end{array}
Given E° Zn2+/Zn = – 0-763 and E°Cd2+/Cd = -0.403
Chapter: [0.066] Corrosion
Define the following terms:
(1) Equivalent conductivity
(2) Corrosion of metals
Chapter: [0.064] Electrolytic conductance [0.064] Electrolytic conductance
The specific conductivity of a solution containing 5 g of anhydrous BaCl2 (mol. wt. = 208) in 1000 cm3 of a solution is found to be 0.0058 ohm-1 cm-1. Calculate the molar and equivalent conductivity of the solution.
Chapter: [0.064] Electrolytic conductance [0.064] Electrolytic conductance
What is an electrochemical series? How is it useful in predicting whether a metal can liberate hydrogen from acid or not?
Chapter: [0.062] Galvanic cells, mechanism of current production in a galvanic cell;
Explain why:
(1) Nitrogen does not form pentahalides.
(2) Helium is used for filling weather balloons.
(3) ICl is more reactive than I2.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Reversible reactions and dynamic equilibrium
Draw the structures of the following:
(1) HClO4
(2) H3PO3
Chapter: [0.08] Chemistry of p-Block Elements: Group 16, 17, 18
Explain why:
(1) Mercury loses its meniscus in contact with ozone.
(2) Halogens are coloured and the colour deepens on moving down in the group from fluorine to iodine.
(3) Hydride of sulphur is a gas while hydride of oxygen is a liquid.
Chapter: [0.09] Preparation/ Manufacture, Properties and Uses of Compounds of Groups 16, 17, – Ozone, Sulphur Dioxide, Sulphuric Acid, Hydrochloric Acid
Complete and balance the following reactions:
(1) NaCl + MnO2 + H2SO4 → _____ + _____ + ______ + _____
(2) KMnO4 + SO2 + H2O → _____ + ______ + ______ + ______
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Give balanced equations for the following reactions:
(1) Benzaldehyde reacts with hydrazine.
(2) Acetic acid reacts with phosphorous pentachloride.
(3) Acetone reacts with sodium bisulphite.
Chapter: [0.131] Carbonyl compounds
Give one chemical test each to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(1) Ethanol and acetic acid
(2) Acetaldehyde and benzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.057] Common ion effect
Write a chemical equation to illustrate the following name reaction:
Clemmensen’s reduction
Chapter: [0.131] Carbonyl compounds
Write a chemical equation to illustrate the following name reaction:
Rosenmund’s reduction
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
Write a chemical equation to illustrate the following name reaction:
HVZ reaction
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Explain why:
(1) Acetaldehyde undergoes aldol condensation but formaldehyde does not.
(2) Acetic acid is a weaker acid as compared to formic acid.
Chapter: [0.057] Common ion effect
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry (Theory) with solutions 2017 - 2018
Previous year Question paper for CISCE Class 12 -2018 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE Class 12.
How CISCE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
