Advertisements
Advertisements
State the principle of an ac generator and explain its working with the help of a labelled diagram. Obtain the expression for the emf induced in a coil. having N turns each of cross-sectional area A, rotating with a constant angular speed 'ω' in a magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Concept: A.C. Generator
An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
Concept: Induced e.m.f. and Induced Current
The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
1) Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for power dissipation in this device.
2) Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
3) Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
Concept: Transformers
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through X is given as
`I = I_0 sin (omega t + pi/2 )`
1) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
2) Draw graphs showing the variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
3) How does the reactance of the device X vary with the frequency of the ac? Show this variation graphically.
4) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
Concept: Peak and Rms Value of Alternating Current Or Voltage
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
Concept: Electromagnetic Spectrum
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index`3/2`, placed in water of refractive index `4/3`.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
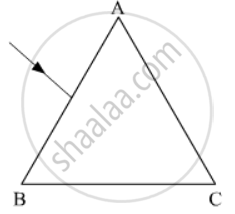
Concept: Total Internal Reflection
Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object.
Concept: Concave Mirror
Obtain the mirror formula and write the expression for the linear magnification.
Concept: Concave Mirror
When a tiny circular obstacle is placed in the path of light from a distant source, a bright spot is seen at the centre of the shadow of the obstacle. Explain why?
Concept: Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
Concept: Polarisation
If one of two identical slits producing interference in Young’s experiment is covered with glass, so that the light intensity passing through it is reduced to 50%, find the ratio of the maximum and minimum intensity of the fringe in the interference pattern.
Concept: Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment
What kind of fringes do you expect to observe if white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
Concept: Refraction of Monochromatic Light
Using Huygens’ principle, verify the laws of reflection at a plane surface.
Concept: Huygens' Principle
If light of wavelength 412.5 nm is incident on each of the metals given below, which ones will show photoelectric emission and why?
| Metal | Work Function (eV) |
| Na | 1.92 |
| K | 2.15 |
| Ca | 3.20 |
| Mo | 4.17 |
Concept: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light
A hydrogen atom initially in the ground level absorbs a photon, which excites it to the n = 4 level. Determine the wavelength and frequency of the photon.
Concept: Energy Levels
State Bohr's postulate to define stable orbits in the hydrogen atom. How does de Broglie's hypothesis explain the stability of these orbits?
Concept: Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
Concept: Law of Radioactive Decay
Explain the processes of nuclear fission and nuclear fusion by using the plot of binding energy per nucleon (BE/A) versus the mass number A
Concept: Nuclear Energy > Nuclear Fusion – Energy Generation in Stars
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier. Explain its working showing its input and output waveforms.
Concept: Application of Junction Diode as a Rectifier
A student wants to use two p-n junction diodes to convert alternating current into direct current. Draw the labelled circuit diagram she would use and explain how it works.
Concept: p-n Junction
