Please select a subject first
Advertisements
Advertisements
Read the passage given below:
People tend to amass possessions, sometimes without being aware of doing so. They can have a delightful surprise when they find something useful which they did not know they owned. Those who never have to change house become indiscriminate collectors of what can only be described as clutter. They leave unwanted objects in drawers, cupboards, and attics for years in the belief that they may one day need them. Old people also accumulate belongings for two other reasons, lack of physical and mental energy, and sentiment. Things owned for a long time are full of associations with the past, perhaps with the relatives who are dead, and so they gradually acquire a sentimental value.
Some things are collected deliberately in an attempt to avoid wastage. Among these are string and brown paper, kept by thrifty people when a parcel has been opened. Collecting small items can be mania. A lady cuts out from newspaper sketches of model clothes that she would like to buy if she had money. As she is not rich, the chances are that she will never be able to afford such purchases. It is a harmless habit, but it litters up her desk.
Collecting as a serious hobby is quite different and has many advantages. It provides relaxation for leisure hours, as just looking at one’s treasure is always a joy. One doesn’t have to go out for amusement as the collection is housed at home. Whatever it consists of - stamps, records, first editions of books, china – there is always something to do in connection with it, from finding the right place for the latest addition to verifying facts in reference books. This hobby educates one not only in the chosen subject but also in general matters which have some bearing on it.
There are other benefits also. One gets to meet like-minded collectors to get advice, compare notes, exchange articles, to show off one’s latest find. So one’s circle of friends grows. Soon the hobby leads to traveling, perhaps a meeting in another town, possibly a trip abroad in search of a rare specimen, for collectors are not confined to one country. Over the years one may well become an authority on one’s hobby and will probably be asked to give informal talks to little gatherings and then, if successful, to larger audiences.
(a) On the basis of your understanding of the above passage make notes on it using headings and sub-headings. Use recognizable abbreviations (wherever necessary-minimum four) and a format you consider suitable. Also, supply an appropriate title to it.
(b) Write a summary of the passage in about 80 words.
Concept: Unseen Passage Comprehension
Define electric flux.
Concept: Electric Flux
If the point charge is now moved to a distance 'd' from the centre of the square and the side of the square is doubled, explain how the electric flux will be affected.
Concept: Applications of Gauss’s Law
Draw a graph to show the variation of E with perpendicular distance r from the line of charge.
Concept: Applications of Gauss’s Law
Find the work done in bringing a charge q from perpendicular distance r1 to r2 (r2 > r1)
Concept: Applications of Gauss’s Law
Four point charges Q, q, Q and q are placed at the corners of a square of side 'a' as shown in the figure.
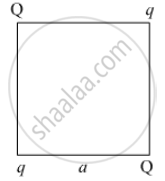
Find the
1) resultant electric force on a charge Q, and
2) potential energy of this system.
Concept: Potential Energy of a System of Charges
Two electric bulbs P and Q have their resistances in the ratio of 1 : 2. They are connected in series across a battery. Find the ratio of the power dissipation in these bulbs
Concept: Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
A 10 V cell of negligible internal resistance is connected in parallel across a battery of emf 200 V and internal resistance 38 Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of current in the circuit.
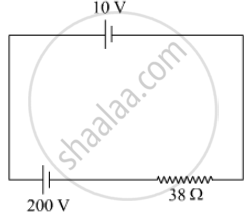
Concept: Cells, Emf, Internal Resistance
Define the term 'conductivity' of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit.
Concept: Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity
A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency?
Concept: Motion in Combined Electric and Magnetic Fields > Cyclotron
A bar magnet of magnetic moment 6 J/T is aligned at 60° with a uniform external magnetic field of 0·44 T Calculate
a) the work done in turning the magnet to align its magnetic moment
i) normal to the magnetic field,
ii) opposite to the magnetic field, and
b) the torque on the magnet in the final orientation in case (ii).
Concept: Magnetic Diapole
An iron ring of relative permeability µr has windings of insulated copper wire of n turns per meter. When the current in the windings is I, find the expression for the magnetic field in the ring.
Concept: Solenoid and the Toroid - the Toroid
The susceptibility of a magnetic material is 0·9853. Identify the type of magnetic material. Draw the modification of the field pattern on keeping a piece of this material in a uniform magnetic field.
Concept: Magnetic Properties of Materials
State the principle of an ac generator and explain its working with the help of a labelled diagram. Obtain the expression for the emf induced in a coil. having N turns each of cross-sectional area A, rotating with a constant angular speed 'ω' in a magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Concept: A.C. Generator
An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of 900 km/hour. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of 20 m. The horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field is 5 × 10–4 T and the angle of dip is 30°.
Concept: Induced e.m.f. and Induced Current
The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
1) Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for power dissipation in this device.
2) Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
3) Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
Concept: Transformers
A device X is connected across an ac source of voltage V = V0 sin ωt. The current through X is given as
`I = I_0 sin (omega t + pi/2 )`
1) Identify the device X and write the expression for its reactance.
2) Draw graphs showing the variation of voltage and current with time over one cycle of ac, for X.
3) How does the reactance of the device X vary with the frequency of the ac? Show this variation graphically.
4) Draw the phasor diagram for the device X.
Concept: Peak and Rms Value of Alternating Current Or Voltage
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
Concept: Electromagnetic Spectrum
The figure shows a ray of light falling normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism having refractive index`3/2`, placed in water of refractive index `4/3`.Will this ray suffer total internal reflection on striking the face AC? Justify your answer.
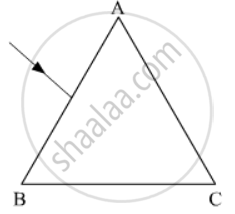
Concept: Total Internal Reflection
Draw a ray diagram to show image formation when the concave mirror produces a real, inverted and magnified image of the object.
Concept: Concave Mirror
