Advertisements
Advertisements
A gas in equilibrium has uniform density and pressure throughout its volume. This is strictly true only if there are no external influences. A gas column under gravity, for example, does not have the uniform density (and pressure). As you might expect, its density decreases with height. The precise dependence is given by the so-called law of atmospheres
n2 = n1 exp [-mg (h2 – h1)/ kBT]
Where n2, n1 refer to number density at heights h2 and h1 respectively. Use this relation to derive the equation for sedimentation equilibrium of a suspension in a liquid column:
n2 = n1 exp [-mg NA(ρ - P′) (h2 –h1)/ (ρRT)]
Where ρ is the density of the suspended particle, and ρ’ that of surrounding medium. [NA is Avogadro’s number, and R the universal gas constant.] [Hint: Use Archimedes principle to find the apparent weight of the suspended particle.]
Concept: undefined > undefined
Which of the following example represent periodic motion?
An arrow released from a bow.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Advertisements
Which of the following example represent (nearly) simple harmonic motion and which represent periodic but not simple harmonic motion?
General vibrations of a polyatomic molecule about its equilibrium position.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Figure depicts four x-t plots for linear motion of a particle. Which of the plots represent periodic motion? What is the period of motion (in case of periodic motion)?
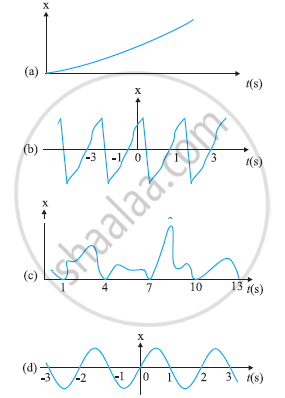
Concept: undefined > undefined
The piston in the cylinder head of a locomotive has a stroke (twice the amplitude) of 1.0 m. If the piston moves with simple harmonic motion with an angular frequency of 200 rad/min, what is its maximum speed?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
(b) What are its amplitude and frequency?
(c) What is the initial phase at the origin?
(d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
Concept: undefined > undefined
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = cos x sin t + cos 2x sin 2t
Concept: undefined > undefined
Explain why (or how): Bats can ascertain distances, directions, nature, and sizes of the obstacles without any “eyes”,
Concept: undefined > undefined
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
Concept: undefined > undefined
Explain why (or how) The shape of a pulse gets distorted during propagation in a dispersive medium.
Concept: undefined > undefined
Two projectiles A and B are projected with angle of projection 15° for the projectile A and 45° for the projectile B. If RA and RB be the horizontal range for the two projectiles, then
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle moves along the X-axis as x = u (t − 2 s) + a (t − 2 s)2.
(a) the initial velocity of the particle is u
(b) the acceleration of the particle is a
(c) the acceleration of the particle is 2a
(d) at t = 2 s particle is at the origin.
Concept: undefined > undefined
The geostationary orbit of the earth is at a distance of about 36000 km from the earth's surface. Find the weight of a 120-kg equipment placed in a geostationary satellite. The radius of the earth is 6400 km.
Concept: undefined > undefined
A man has to go 50 m due north, 40 m due east and 20 m due south to reach a field. (a) What distance he has to walk to reach the field? (b) What is his displacement from his house to the field?
Concept: undefined > undefined
A particle starts from the origin, goes along the X-axis to the point (20 m, 0) and then return along the same line to the point (−20 m, 0). Find the distance and displacement of the particle during the trip.
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the acceleration
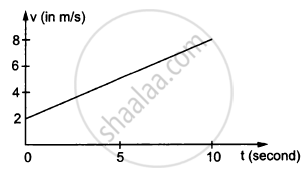
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the distance travelled in 0 to 10s
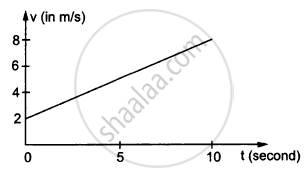
Concept: undefined > undefined
In the following figure Shows the graph of velocity versus time for a particle going along the X-axis. Find the displacement in 0 to 10 s.
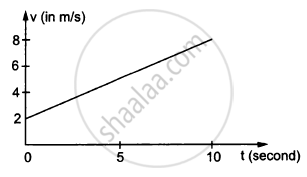
Concept: undefined > undefined
When you lift a box from the floor and put it on an almirah the potential energy of the box increases, but there is no change in its kinetic energy. Is it a violation of conservation of energy?
Concept: undefined > undefined
