Topics
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower - a Fascinating Organ of Angiosperms
- Parts of Flower
- Accessory Organs
- Essential Parts of Flower: Androecium
- Essential Parts of Flower: Gynoecium
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Pre-fertilisation in Flowering Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Anther
- Transverse Section of Mature Anther (Microsporangium)
- Microsporogenesis
- Microspores and Pollen Grains
- Development of Male Gametophyte
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Pollen Grains
- Structure of Ovule (Megasporangium)
- Types of Ovules
- Megasporogenesis
- Development of Female Gametophyte or Embryo Sac
- Pollination
- Outbreeding Devices
- Artificial Hybridization
- Kinds of Pollination
- Self Pollination (Autogamy)
- Cross Pollination
- Agents of Pollination
- Abiotic Agents
- Biotic Agents
- Fertilization Process
- Fertilization Process
- Post Fertilisation in Plant: Structures and Events
- Development of Endosperm
- Post Fertilization in Plant: Development of Embryo (Embryogeny)
- Development of Seed
- Development of Fruit
- Apomixis
- Polyembryony
Reproduction in Organisms
- Life Span of Organisms
- Maximum Life Span of Organisms
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Types of Reproduction
- Asexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Asexual Reproduction in Plant
- Asexual Reproduction in Animal
- Budding
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Natural Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Artificial Vegetative Reproduction
- Fission
- Budding
- Sporulation (Sporogenesis)
- Fragmentation
- Different Phases in Sexual Reproduction
- Sexual Reproduction in Animals
- Pre-fertilisation Events in Organisms
- Fertilisation in Organisms
- Post-fertilisation Events in Organisms
Reproduction
Genetics and Evolution
Human Reproduction
Reproductive Health
Biology and Human Welfare
Environmental Issues
- Environmental Issues
- Prevention of Air Pollution
- Controlling Vehicular Air Pollution: a Case Study of Delhi
- Introduction of Water Pollution and Its Control
- Effects of Domestic Sewage and Industrial Effluents on Water
- A Case Study of Integrated Waste Water Treatment
- Solid Wastes
- Agrochemicals and Their Effects
- Radioactive Wastes
- Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
- Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
- Degradation by Improper Resource Utilisation and Maintenance
- Deforestation and Its Causes
- Radioactive Waste Management and E-waste
- Solid Waste Management
- Noise Pollution
- Environmental Issues
Biotechnology
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Introduction of Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelism
- Terminology Related to Mendelism
- Mendel’s experiments on pea plant
- Monohybrid Cross
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Punnett Square
- Back Cross and Test Cross
- Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity
- The Law of Dominance
- The Law of Segregation (Law of Purity of Gametes)
- The Law of Independent Assortment
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics
- Extensions of Mendelian Genetics (Deviation from Mendelism)
- Intragenic Interactions - Incomplete Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Dominance
- Intragenic Interactions - Codominance
- Multiple Alleles
- Intragenic Interactions - Pleiotropy
- Polygenic Inheritance
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
- Historical Development of Chromosome Theory
- Comparison Between Gene and Chromosome Behaviour
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Segregation
- Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance: Law of Independent Assortment
- Linkage and Recombination
- Sex Determination
- Sex Determination in Some Insects
- Sex Determination in Human
- Sex Determination in Birds
- Sex Determination in Honey Bees
- Concept of Mutation
- Pedigree Analysis
- Genetic Disorders
- Mendelian Genetics
- Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Heredity and Variation
- Linkage and Crossing Over
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Introduction of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure
- Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
- Packaging of DNA Helix
- Search for Genetic Material
- Introduction of Search for Genetic Material
- The Genetic Material is a DNA
- Properties of Genetic Material (DNA Versus RNA)
- The RNA World
- DNA Replication
- The Experimental Proof
- The Machinery and the Enzymes
- Protein Synthesis
- Introduction of Transcription
- Transcription Unit
- Transcription Unit and the Gene
- Types of RNA and the Process of Transcription
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- Genetic Code
- tRNA – the Adapter Molecule
- Translation
- Regulation of Gene Expression
- Operon Concept
- Human Genome Project
- DNA Fingerprinting Technique
- Structure of DNA and RNA
- Structure of Nucleotide
- Rice Genome Project
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance (Questions)
Ecology
Evolution
- Origin and Evolution of Universe and Earth
- Theories of Origin of Life
- Evolution of Life Forms - a Theory
- Evidences for Biological Evolution
- Theories of Biological Evolution
- Adaptive Radiation
- Organic Evolution
- Hardy Weinberg’s Principle
- Brief Account of Evolution
- Human Evolution
- Darwinism
- Micro and Macro Evolution
- Speciation
- Evolution Stages
- Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution
- Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
- Evolution
Human Health and Diseases
- Introduction of Human Health and Diseases
- Common Diseases in Human Beings
- Immunity
- Types of Immunity
- Vaccination and Immunization
- Allergies (Hypersensitivity)
- Autoimmunity
- Human Immune System
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Cancer
- Introduction of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Adolescence - Drug and Alcohol Abuse
- Addiction and Dependence
- Effects of Drug and Alcohol
- Prevention and Control of Drugs and Alcohol Abuse
- Infectious and Non Infectious Disease
- Maintaining Good Health, Yoga, Excercise
- Human Health and Diseases (Questions)
Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Production
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
- Energy Generation
- Production and Judicious Use
- Microbes in Human Welfare
Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Process and Principles of Biotechnology
- Restriction Enzymes
- Cloning Vectors
- Competent Host (For Transformation with Recombinant DNA)
- Processes of Recombinant DNA Technology
Biotechnology and Its Application
Organisms and Populations
- Introduction of Organisms and Populations
- Ecology (Organism, Population, Community and Biome)
- Introduction of Organisms and Environment
- Major Abiotic Factors
- Responses to Abiotic Factors
- Population Attributes
- Population Growth
- Life History Variation
- Population Interactions
- Population and Ecological Adaptations
- Organisms and Populations (Questions)
Ecosystem
- Ecosystem
- Introduction and Types of Ecosystem
- Ecosystem - Structure and Function
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Concept of Energy Flow in an Ecosystem
- Ecological Pyramids
- Ecological Succession
- Nutrient Cycles
- Ecosystem Services
- Ecosystems Patterns
Biodiversity and Its Conservation
- Biodiversity
- Species on Earth and Species in India
- Patterns of Biodiversity
- Importance of Species Diversity to the Ecosystem
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Endangered Organisms
- Importance of Biodiversity
- Extinction
- Red Data Book
- Biodiversity and Its Conservation (Questions)
Notes
Drugs and Alcohol Abuse:
- Surveys and statistics show that use of drugs and alcohol has been on the rise, especially among the youth.
- This is a major source of concern since it has the potential to create a wide range of negative consequences. This is a major source of concern since it has the potential to create a wide range of negative consequences. Youth could be protected from these harmful behaviour patterns if they were given the proper education and direction.
- The drugs, which are commonly abused are opioids, cannabinoids and coca alkaloids. The majority of these are obtained from flowering plants. Some are obtained from fungi.
1) Opioids:
- Opioids are drugs, which bind to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract.
- The chemical compound diacetylmorphine, sometimes known as smack, is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline substance (heroin).
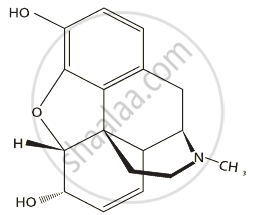
- Morphine is extracted from the latex of Papaver somniferous (poppy plant). It is a sedative or any painkiller. Used in surgery.
2) Heroin:
Heroin, commonly called smack is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine, which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver somniferum. Generally taken by snorting and injection, heroin is a depressant and slows down body functions.
|
Chemical structure of Morphine |
Opium poppy |
3) Cannabinoids:
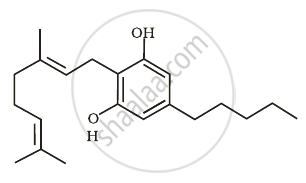
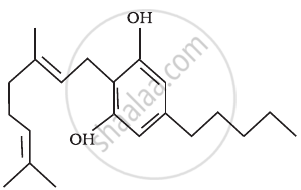
- Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals, which interact with cannabinoid receptors present principally in the brain.
- Natural cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescences of the plant Cannabis sativa.
- Generally taken by inhalation and oral ingestion.
- The flower tops, leaves and the resin of the cannabis plant are used in various combinations to produce marijuana, hashish, charas and ganja.
- These are known for their effects on the cardiovascular system of the body.
- Cannabinoids are abused by some sportspersons.
|
Skeletal structure of cannabinoid molecule |
Leaves of Cannabis sativa |
4) Coca Alkaloid or cocaine (Coke or Crack):
- Cocaine is derived from the coca plant Erythroxylum coca, which is endemic to South America.
- It interferes with the transport of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
- Cocaine, commonly called coke or crack is usually snorted.
- It has a potent stimulating action on the central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy.
- An excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
- Atropa belladona and Datura are two other well-known plants with hallucinogenic characteristics.
- Barbiturates, amphetamines, benzodiazepines, and other related drugs, which are typically prescribed to assist patients live with mental diseases such as depression and sleeplessness, are frequently abused.
- Morphine is a very effective sedative and painkiller and is very useful in patients who have undergone surgery.
- Several hallucinogenic plants, fruits, and seeds have been utilised in folk medicine, religious rites, and rituals around the world for hundreds of years.

Atropa belladonna

Datura
5) Smoking:
- Smoking also paves the way to hard drugs.
- Tobacco has been used by human beings for more than 400 years.
- It is smoked, chewed or used as a snuff.
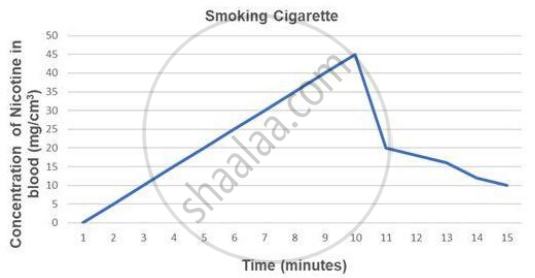
- Tobacco contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Nicotine stimulates the adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation, both of which raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
- Smoking is linked to an increased risk of lung, bladder, and throat cancers, as well as bronchitis, emphysema, coronary heart disease, and gastric ulcers.
- Chewing tobacco has been linked to an increased risk of mouth cancer.
- Smoking raises the concentration of carbon monoxide (CO) in the blood and lowers the concentration of haembound oxygen.
- This results in a lack of oxygen in the body.
- Knowing the risks of smoking and chewing tobacco, as well as the addictive nature of these habits, both the young and elderly should avoid them. To overcome a habit, an addict will need counselling and medical assistance.
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.