Topics
Units and Measurements
- Introduction of Units and Measurements
- System of Units
- Measurement of Length
- Measurement of Mass
- Measurement of Time
- Dimensions and Dimensional Analysis
- Accuracy, Precision and Uncertainty in Measurement
- Errors in Measurements
- Significant Figures
Mathematical Methods
- Vector Analysis
- Vector Operations
- Resolution of Vectors
- Multiplication of Vectors
- Introduction to Calculus
Motion in a Plane
- Introduction to Motion in a Plane
- Rectilinear Motion
- Motion in Two Dimensions-Motion in a Plane
- Uniform Circular Motion (UCM)
Laws of Motion
- Introduction to Laws of Motion
- Aristotle’s Fallacy
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
- Types of Forces
- Work Energy Theorem
- Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum
- Collisions
- Impulse of Force
- Rotational Analogue of a Force - Moment of a Force Or Torque
- Couple and Its Torque
- Mechanical Equilibrium
- Centre of Mass
- Centre of Gravity
Gravitation
- Introduction to Gravitation
- Kepler’s Laws
- Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation
- Measurement of the Gravitational Constant (G)
- Acceleration Due to Gravity (Earth’s Gravitational Acceleration)
- Variation in the Acceleration Due to Gravity with Altitude, Depth, Latitude and Shape
- Gravitational Potential and Potential Energy
- Earth Satellites
Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Introduction to Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Elastic Behavior of Solids
- Stress and Strain
- Hooke’s Law
- Elastic Modulus
- Stress-strain Curve
- Strain Energy
- Hardness
- Friction in Solids
Thermal Properties of Matter
- Introduction to Thermal Properties of Matter
- Heat and Temperature
- Measurement of Temperature
- Absolute Temperature and Ideal Gas Equation
- Thermal Expansion
- Specific Heat Capacity
- Calorimetry
- Change of State
- Heat Transfer
- Newton’s Law of Cooling
Sound
- Introduction to Sound
- Types of Waves
- Common Properties of All Waves
- Transverse Waves and Longitudinal Waves
- Mathematical Expression of a Wave
- The Speed of Travelling Waves
- Principle of Superposition of Waves
- Echo, Reverberation and Acoustics
- Qualities of Sound
- Doppler Effect
Optics
- Introduction to Ray Optics
- Nature of Light
- Ray Optics Or Geometrical Optics
- Reflection
- Refraction
- Total Internal Reflection
- Refraction at a Spherical Surface and Lenses
- Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum
- Some Natural Phenomena Due to Sunlight
- Defects of Lenses (Aberrations of Optical Images)
- Optical Instruments
- Optical Instruments: Simple Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Compound Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Telescope
Electrostatics
- Introduction to Electrostatics
- Electric Charges
- Basic Properties of Electric Charge
- Coulomb’s Law - Force Between Two Point Charges
- Principle of Superposition
- Electric Field
- Electric Flux
- Gauss’s Law
- Electric Dipole
- Continuous Distribution of Charges
Electric Current Through Conductors
- Electric Current
- Flow of Current Through a Conductor
- Drift Speed
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Electrical Power
- Resistors
- Specific Resistance (Resistivity)
- Variation of Resistance with Temperature
- Electromotive Force (emf)
- Combination of Cells in Series and in Parallel
- Types of Cells
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
Magnetism
- Introduction to Magnetism
- Magnetic Lines of Force and Magnetic Field
- The Bar Magnet
- Gauss' Law of Magnetism
- The Earth’s Magnetism
Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System
- EM Wave
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Propagation of EM Waves
- Introduction to Communication System
- Modulation
Semiconductors
- Introduction to Semiconductors
- Electrical Conduction in Solids
- Band Theory of Solids
- Intrinsic Semiconductor
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- p-n Junction
- A p-n Junction Diode
- Basics of Semiconductor Devices
- Applications of Semiconductors and P-n Junction Diode
- Thermistor
Resistors
In electronic circuits, materials like copper and aluminium are conductors with negligible resistance, while paper and ceramic are insulators with high resistance. Carbon, with varying resistance, is used as a resistor, measured in Ohms (Ω). Resistance opposes electric current, limiting current, dropping voltage, and dividing voltage in circuits. Combined with capacitors, resistors function as filters or create time delays.
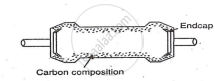
Carbon Composition Resistors (Fixed Resistors)
Carbon composition resistors are widely used in electronic circuits. They range from 1Ω to about 20MΩ, with power ratings of 1/8W to 2W. These resistors are low-cost and small-sized, commonly found in laboratories.
Construction
- Materials: Made by mixing carbon granules with a binding material.
- Forming: Molded into a cylindrical shape.
- Leads: Tinned copper wire leads are inserted at both ends.
- Sealing: The structure is sealed with a non-conducting coating.
The cost of a resistor is based on its wattage, not its resistance value.
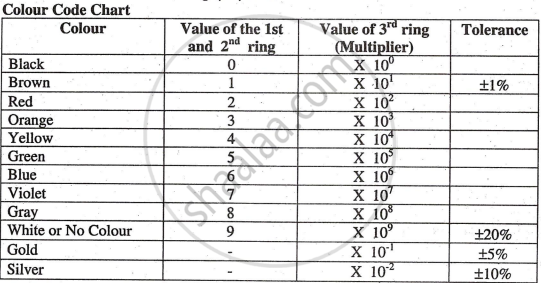
Color Coding of Carbon Resistor
Another feature of carbon resistors is the color code system, indicating value and tolerance. Tolerance shows the maximum deviation from the stated value, expressed as a percentage. For example, a 100 Ω resistor with ±5% tolerance ranges from 95 Ω to 105 Ω. In color code method, the first two rings indicate the first two digits, and the third ring indicates the multiplier. The fourth ring is used to indicate its tolerance
Wire Wound Resistors (Fixed Resistors)
Wire wound resistors are used for high current control and require stable, accurate resistance values.
a)Construction: They are made by wrapping a resistive wire like nichrome or manganin around a ceramic core, with wire ends attached to metal contacts. The structure is coated with vitreous enamel to protect the resistor and dissipate heat.
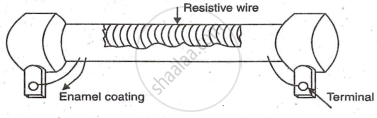
b) Drawbacks: Large size, limiting higher values.
c) Advantage: High power handling capacity.
d) Range: Resistance: Fraction of ohms to 100 kΩ.
e) Power rating: 5 W to 200 W.
Carbon Type Potentiometers (Variable Resistors)
Variable resistors, or rheostats, are known as potentiometers or "pots" in low current circuits. They consist of a wiper moving on a circular carbon resistive track attached to shaft, which can be metal or plastic.
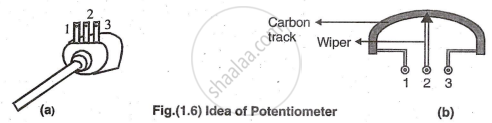
Made with resistive carbon on a Bakelite piece, potentiometers have three terminals: two fixed (1 and 3) and one variable (2). Connecting terminals 1 and 3 provides maximum resistance, while connecting 1 and 2 or 2 and 3 allows resistance adjustment by rotating the shaft. Resistance varies from zero (wiper at terminal 1) to maximum (wiper fully rotated to the right).
a) Specialty: Low Cost, Used in Radio, TV as volume control, brightness control etc.
b) Range: 1 KΩ to 5 MΩ, Power rating 1/2W to 2W
Wire Wound Potentiometers (Variable Resistors)
The basic principle of a wire wound variable resistor, commonly seen in rheostats, involves winding wire on an open ceramic ring covered with vitreous enamel. Non-linear types use a tapered strip for winding. Resistance varies by sliding the contact.
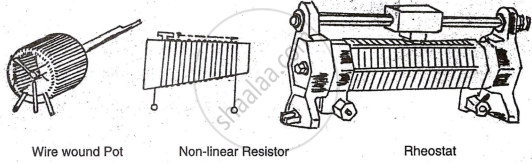
a) Drawback: High cost and large size.
b) Advantage: High power handling capacity and precise resistance adjustment.
c)Construction: Wire wound on a ceramic ring, coated with vitreous enamel, with linear and non-linear (tapered) options.
d)Range: Resistance: 100Ω to 1 MΩ.
Power rating: 2W to 100W.
Other Resistors
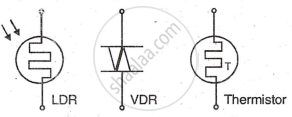
- Thermistor: A thermistor's resistance changes non-linearly with temperature: NTC decreases resistance with heat; PTC increases. Used for temperature measurement/control.
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR): It is a photosensitive device whose resistance decreases with increase in light intensity. Cadmium sulfide material is used for this purpose. LPR is widely used in many applications like automatic street light control, burglar alarm etc.
- Varistor (VDR): A voltage-dependent resistor (varistor) has resistance that varies with voltage. Types include Silicon Carbide and Metal Oxide VDRs. Used for surge suppression in industrial applications and TV circuits.