Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
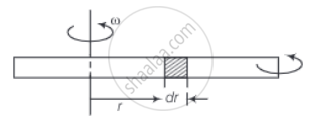
A steel rod of length 2l, cross sectional area A and mass M is set rotating in a horizontal plane about an axis passing through the centre. If Y is the Young’s modulus for steel, find the extension in the length of the rod. (Assume the rod is uniform.)
उत्तर
Consider an element of width dr at t as shown in the diagram.
Let T(r) and T(r + dr) be the tensions at r and r + dr respectively.
Net centrifugal force on the element = ω2rdm ....(Where ω is the angular velocity of the rod)
= ω2rμdr .....(∵ μ = mass/length)
⇒ T(r) – T(r + dr) = μω2rdr
⇒ – dT = μω2rdr ......[∵ Tension and centrifugal forces are opposite]
∴ `- int_(T = 0)^T dT = int_(r = l)^(r= r) μω^2rdr` ......[∵ T = 0 at r = l]
⇒ `T(r) = (μω^2)/2 (l^2 - r^2)`
Let the increase in length of the element dr be Δr
So, Young's modulus Y = `"Stress"/"Strain" = ((T(r))/A)/((Δr)/(dr))`
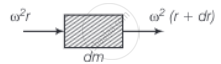
∴ `(Δr)/(dr) = (T(r))/A = (μω^2)/(2YA) (l^2 - r^2)`
∴ `Δr = 1/(YA) (μω^2)/2 (l^2 - r^2)dr`
∴ Δ = Change in length in right part = `1/(YA) (μω^2)/2 int_0^l (l^2 - r^2) dr`
= `(1/(YA)) (μω^2)/2 [t^3 - l^3/3]`
= `1/(3YA) μω^2l^2`
∴ Total change in length = 2Δ = `2/(3YA) μω^2l^2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Figure
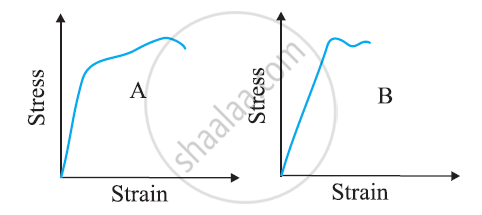
The graphs are drawn to the same scale.
(a) Which of the materials has the greater Young’s modulus?
(b) Which of the two is the stronger material?
Read the following statements below carefully and state, with reasons, if it is true or false
The Young’s modulus of rubber is greater than that of steel;
A wire elongates by 1.0 mm when a load W is hung from it. If this wire goes over a a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends, he elongation of he wire will be
A copper wire of cross-sectional area 0.01 cm2 is under a tension of 20N. Find the decrease in the cross-sectional area. Young modulus of copper = 1.1 × 1011 N m−2 and Poisson ratio = 0.32.
`["Hint" : (Delta"A")/"A"=2(Delta"r")/"r"]`
Young's modulus of a perfectly rigid body is ______.
A rigid bar of mass M is supported symmetrically by three wires each of length l. Those at each end are of copper and the middle one is of iron. The ratio of their diameters, if each is to have the same tension, is equal to ______.
If the yield strength of steel is 2.5 × 108 Nm–2, what is the maximum weight that can be hung at the lower end of the wire?
A metal wire of length L, area of cross section A and Young's modulus Y behaves as a spring of spring constant k given by:
A uniform metal rod of 2 mm2 cross section is heated from 0°C to 20°C. The coefficient of linear expansion of the rod is 12 × 10-6/°C, it's Young's modulus is 1011 N/m2. The energy stored per unit volume of the rod is ______.
The force required to stretch a wire of cross section 1 cm2 to double its length will be ______.
(Given Young's modulus of the wire = 2 × 1011 N/m2)
