Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A variable plane which remains at a constant distance 3p from the origin cuts the coordinate axes at A, B, C. Show that the locus of the centroid of triangle ABC is `1/x^2 + 1/y^2 + 1/z^2 = 1/p^2`
उत्तर
Let the equation of the plane be
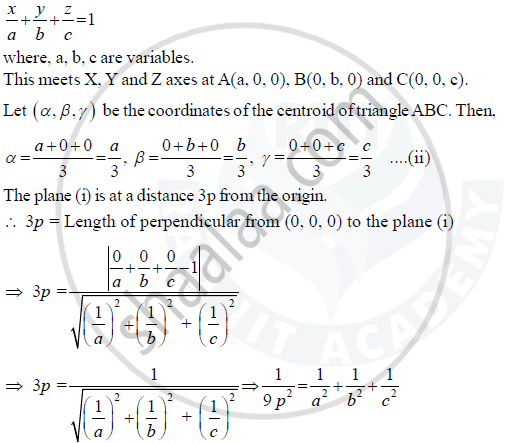
From (ii), we have
a = 3α ,b = 3β and c = 3γ
Substituting the values of a, b, c in (iii), we obtain
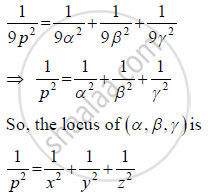
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the sum of intercepts cut off by the plane `vecr.(2hati+hatj-k)-5=0` on the three axes
Find the intercepts cut off by the plane 2x + y – z = 5.
Prove that if a plane has the intercepts a, b, c and is at a distance of P units from the origin, then `1/a^2 + 1/b^2 + 1/c^2 = 1/p^2`
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
4x + 3y − 6z − 12 = 0
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
2x + 3y − z = 6
Reduce the equations of the following planes to intercept form and find the intercepts on the coordinate axes.
2x − y + z = 5
Find the equation of a plane which meets the axes at A, B and C, given that the centroid of the triangle ABC is the point (α, β, γ).
Find the equation of the plane passing through the point (2, 4, 6) and making equal intercepts on the coordinate axes.
Find the equation of the plane with intercept 3 on the y-axis and parallel to the ZOX plane.
Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z − 4 = 0 and 2x + y − z + 5 = 0 and which is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y − 6z+ 8 = 0.
Find the equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z + 4 = 0 and x − y + z + 3 = 0 and passing through the origin.
Find the vector equation (in scalar product form) of the plane containing the line of intersection of the planes x − 3y + 2z − 5 = 0 and 2x − y + 3z − 1 = 0 and passing through (1, −2, 3).
Find the equation of the plane that is perpendicular to the plane 5x + 3y + 6z + 8 = 0 and which contains the line of intersection of the planes x + 2y + 3z − 4 = 0, 2x + y − z + 5 = 0.
Find the equation of the plane passing through the intersection of the planes 2x + 3y − z+ 1 = 0 and x + y − 2z + 3 = 0 and perpendicular to the plane 3x − y − 2z − 4 = 0.
Find the equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} \right) + 6 = 0 \text{ and } \vec{r} \cdot \left( 3 \hat{i} - \hat{j} - 4 \hat{k} \right) = 0,\] which is at a unit distance from the origin.
Find the equation of the plane that contains the line of intersection of the planes \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( \hat{i} + 2 \hat{j} + 3 \hat{k} \right) - 4 = 0 \text{ and } \vec{r} \cdot \left( 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} - \hat{k} \right) + 5 = 0\] and which is perpendicular to the plane \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( 5 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} - 6 \hat{k} \right) + 8 = 0 .\]
Find the vector equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes x + y+ z = 1 and 2x + 3y + 4z = 5 which is perpendicular to the plane x − y + z = 0.
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the intersection of the planes
\[\vec{r} \cdot \left( \hat{ i } + \hat{ j }+ \hat{ k }\right) = \text{ 6 and }\vec{r} \cdot \left( \text{ 2 } \hat{ i} +\text{ 3 } \hat{ j } + \text{ 4 } \hat{ k } \right) = - 5\] and the point (1, 1, 1).
Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planes x \[+\] 2y \[+\] 3 \[z - \] 4 \[=\] 0 and 2 \[x + y - z\] \[+\] 5 \[=\] 0 and whose x-intercept is twice its z-intercept. Hence, write the equation of the plane passing through the point (2, 3, \[-\] 1) and parallel to the plane obtained above.
Find the equation of the plane through the line of intersection of the planes \[x + y + z =\]1 and 2x \[+\] 3 \[+\] y \[+\] 4\[z =\] 5 and twice of its \[y\] -intercept is equal to three times its \[z\]-intercept
Find the length of the perpendicular from origin to the plane `vecr. (3i - 4j-12hatk)+39 = 0`
Find the locus of a complex number, z = x + iy, satisfying the relation `|[ z -3i}/{z +3i]| ≤ sqrt2 `. Illustrate the locus of z in the Argand plane.
A plane passes through the points (2, 0, 0) (0, 3, 0) and (0, 0, 4). The equation of plane is ______.
The equation of the plane which is parallel to 2x − 3y + z = 0 and which passes through (1, −1, 2) is:
The intercepts made on the coordinate axes by the plane 2x + y − 2z = 3 are:
