Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An experimenter's diary reads as follows: "A charged particle is projected in a magnetic field of `(7.0 vec i - 3.0 vecj)xx 10^-3 `T. The acceleration of the particle is found to be `(x veci + 7.0 vecj )` The number to the left of i in the last expression was not readable. What can this number be?
उत्तर
Given,
Magnetic field, B = (7.0i − 3.0j) × 10−3 T
Acceleration of the particle, a = (xi + 7j) × 10−6 m/s2
We have denoted the unidentified number as x.
B and a are perpendicular to each other. (Because magnetic force always acts perpendicular to the motion of the particle)
So, the dot product of the two quantities should be zero.
That is, B.a = 0
⇒ 7x × 10−3 × 10−6 − 3 × 10−3 × 7 × 10−6 = 0
⇒ 7x − 21 = 0
`x = 21/7 = 3`
Acceleration of the particle is (3i + 7j) × 10−6 m/s2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the expression, in a vector form, for the Lorentz magnetic force \[\vec{F}\] due to a charge moving with velocity \[\vec{V}\] in a magnetic field \[\vec{B}\]. What is the direction of the magnetic force?
Show that the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a magnetic field remains constant.
A neutron, an electron and an alpha particle, moving with equal velocities, enter a uniform magnetic field going into the plane of the paper, as shown. Trace their paths in the field and justify your answer.
A proton and an α-particle move perpendicular to a magnetic field. Find the ratio of radii of circular paths described by them when both have (i) equal velocities, and (ii) equal kinetic energy.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
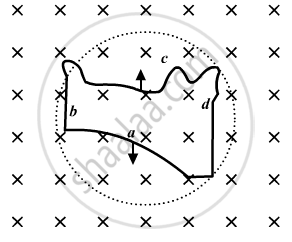
A flexible wire of irregular shape, abcd, as shown in the figure, turns into a circular shape when placed in a region of magnetic field which is directed normal to the plane of the loop away from the reader. Predict the direction of the induced current in the wire.
A proton and a deuteron having equal momenta enter in a region of a uniform magnetic field at right angle to the direction of a the field. Depict their trajectories in the field.
A charged particle moves in a uniform magnetic field. The velocity of the particle at some instant makes an acute angle with the magnetic field. The path of the particle will be
Consider three quantities \[x = E/B, y = \sqrt{1/ \mu_0 \epsilon_0}\] and \[z = \frac{l}{CR}\] . Here, l is the length of a wire, C is a capacitance and R is a resistance. All other symbols have standard meanings.
(a) x, y have the same dimensions.
(b) y, z have the same dimensions.
(c) z, x have the same dimensions.
(d) None of the three pairs have the same dimensions.
When a proton is released from rest in a room, it starts with an initial acceleration a0towards west. When it is projected towards north with a speed v0, it moves with an initial acceleration 3a0 towards west. Find the electric field and the maximum possible magnetic field in the room.
A current of 2 A enters at the corner d of a square frame abcd of side 20 cm and leaves at the opposite corner b. A magnetic field B = 0.1 T exists in the space in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude and direction of the magnetic forces on the four sides of the frame.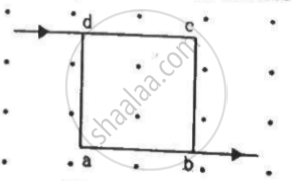
Prove that the force acting on a current-carrying wire, joining two fixed points a and b in a uniform magnetic field, is independent of the shape of the wire.
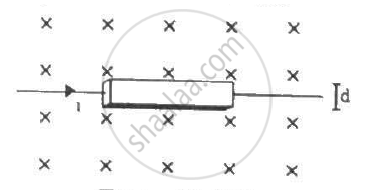
A current i is passed through a silver strip of width d and area of cross-section A. The number of free electrons per unit volume is n. (a) Find the drift velocity v of the electrons. (b) If a magnetic field B exists in the region, as shown in the figure, what is the average magnetic force on the free electrons? (c) Due to the magnetic force, the free electrons get accumulated on one side of the conductor along its length. This produces a transverse electric field in the conductor, which opposes the magnetic force on the electrons. Find the magnitude of the electric field which will stop further accumulation of electrons. (d) What will be the potential difference developed across the width of the conductor due to the electron-accumulation? The appearance of a transverse emf, when a current-carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field, is called Hall effect.
A circular coil of radius 2.0 cm has 500 turns and carries a current of 1.0 A. Its axis makes an angle of 30° with the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T that exists in the space. Find the torque acting on the coil.
A proton is projected with a velocity of 3 × 106 m s−1 perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of 0.6 T. Find the acceleration of the proton.
A proton projected in a magnetic field of 0.020 T travels along a helical path of radius 5.0 cm and pitch 20 cm. Find the components of the velocity of the proton along and perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take the mass of the proton = 1.6 × 10−27 kg
An electron is emitted with negligible speed from the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor charged to a potential difference V. The separation between the plates is dand a magnetic field B exists in the space, as shown in the figure. Show that the electron will fail to strike the upper plates if `d > ((2m_eV)/(eB_0^2))^(1/2)`
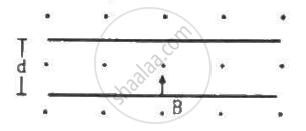
When does a moving charged particle nor experience any force while moving through a uniform magnetic field?
A uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T exists in a cylindrical region of radius 10.0 cm, its direction parallel to the axis along east to west. A wire carrying current of 7.0 A in the north to south direction passes through this region. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on the wire if,
(a) the wire intersects the axis,
(b) the wire is turned from N-S to northeast-northwest direction,
(c) the wire in the N-S direction is lowered from the axis by a distance of 6.0 cm?
