Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Choose the correct alternatives:
- For a general rotational motion, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω need not be parallel.
- For a rotational motion about a fixed axis, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion , momentum p and velocity v are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion, acceleration a and velocity v are always parallel.
उत्तर
a and c
Explanation:
- For a general rotational motion where the axis of rotation is not symmetric. Angular momentum Z and angular velocity 0) need not be parallel. The wobbly motion of a wheel rotating about an axis inclined at a small angle to the symmetry axis of the wheel represents a situation where angular momentum and angular velocity are not parallel.
- Fixed axis should pass through CM of the body, so it is not necessary for angular momentum Z and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- As we know in a general translational motion linear momentum is given by, p = mv, hence, the direction of p is always along v.
- In projectile motion, v and a are not always parallel.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
A ladder is resting with one end on a vertical wall and the other end on a horizontal floor. If it more likely to slip when a man stands near the bottom or near the top?
Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in the following figure about the point O.

A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
The ratio of the acceleration for a solid sphere (mass m and radius R) rolling down an incline of angle θ without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is, ______
State conservation of angular momentum.
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
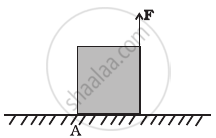
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
A door is hinged at one end and is free to rotate about a vertical axis (Figure). Does its weight cause any torque about this axis? Give reason for your answer.
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by
`vecr = 10alphat^2hati + 5beta(t - 5)hatj`
Where α and β are dimensional constants.
The angular momentum of the particle becomes the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
