Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
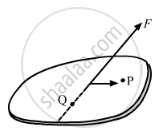
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
उत्तर
No, it is not necessary that the torque about any other point be zero if it is zero about one point.
Let \[\overrightarrow{F}\] be the resultant force due to all the forces acting on the plane of the body. Therefore, torque due to force \vec{F} at any point will be the resultant torque . Now, we see that the torque due to \[\overrightarrow{F}\] at point Q will be zero because Q lies on the line of support of the force F but the torque due to force \[\overrightarrow{F}\] will not be zero along the point P.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l of a particle, whose position vector is r with components x, y, z and momentum is p with components px, py and 'p_z`. Show that if the particle moves only in the x-y plane the angular momentum has only a z-component.
Two particles, each of mass m and speed v, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by a distance d. Show that the angular momentum vector of the two particle system is the same whatever be the point about which the angular momentum is taken.
A solid cylinder of mass 20 kg rotates about its axis with angular speed 100 rad s–1. The radius of the cylinder is 0.25 m. What is the kinetic energy associated with the rotation of the cylinder? What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of the cylinder about its axis?
A heavy particle of mass m falls freely near the earth's surface. What is the torque acting on this particle about a point 50 cm east to the line of motion? Does this torque produce any angular acceleration in the particle?
If several forces act on a particle, the total torque on the particle may be obtained by first finding the resultant force and then taking torque of this resultant. Prove this. Is this result valid for the forces acting on different particles of a body in such a way that their lines of action intersect at a common point?
A body is in translational equilibrium under the action of coplanar forces. If the torque of these forces is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will also be zero about any other point?
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis though the pivot. A horizontal force F is applied on the free end in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The quantities, that do not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are ________________ .
A flywheel of moment of inertia 5⋅0 kg-m2 is rotated at a speed of 60 rad/s. Because of the friction at the axle it comes to rest in 5⋅0 minutes. Find (a) the average torque of the friction (b) the total work done by the friction and (c) the angular momentum of the wheel 1 minute before it stops rotating.
A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
Define torque and mention its unit.
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
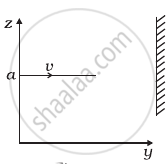
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is ______.
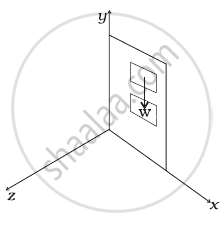
A door is hinged at one end and is free to rotate about a vertical axis (Figure). Does its weight cause any torque about this axis? Give reason for your answer.
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by
`vecr = 10alphat^2hati + 5beta(t - 5)hatj`
Where α and β are dimensional constants.
The angular momentum of the particle becomes the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
Angular momentum of a single particle moving with constant speed along the circular path ______.
