Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
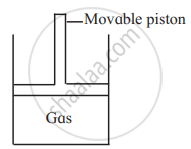
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if pressure is increased from 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar at a constant temperature.
उत्तर
At constant T, P ∝ `1/"V"`
Since, pressure doubles, the volume will become half.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−15° C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
25° C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−197° C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
273° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
10 atmosphere
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert exactly 1.5 atm to pascals
Convert 89 kPa to newton per square metre (Nm−2)
Convert −100° C to kelvin
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
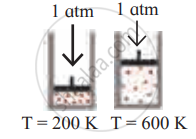 |
______________ |
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
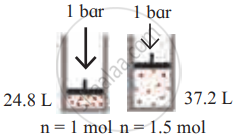 |
______________ |
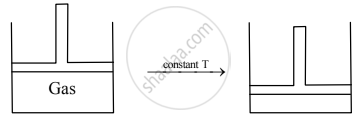
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.

Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 400 K to 300 K, and pressure is decreased from 4 bar to 3 bar.
Write the statement for Charles’ law
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Identify the law.
Solve the following.
At 0°C, a gas occupies 22.4 liters. How much hot must be the gas in celsius and in kelvin to reach a volume of 25.0 liters?
Use of hot air balloon in sports and meteorological observation is an application of
Name two items that can serve as a model for Gay Lusaac’s law and explain.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
For a given mass of an ideal gas, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
Volume of a balloon at 25°C and 1 bar pressure is 2.27 L. If the pressure of the gas in balloon is reduced to 0.227 bar, what is the rise in volume of a gas?
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 2 dm3 at STP. At what temperature the volume of gas becomes double, keeping the pressure constant?
At what temperature the volume of a gas becomes absolutely zero?
The volume of 400 cm3 chlorine gas at 400 mm of Hg is decreased to 200 cm3 at constant temperature. What is the new pressure of gas?
10 g of gas at one atomospheric pressure is cooled from 273.15°C to 0°C keeping the volume constant. What is the final pressure?
At what temperature, the volume of gas would become zero?
The number of molecules in 8.96 litres of gas at 0°C and 1 atm. pressure is approximately ______.
