Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Identify the law.
उत्तर
The graph represents Boyle’s law as it gives a relation between pressure and volume at a constant temperature.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
Answer in one sentence.
A bubble of methane gas rises from the bottom of the North sea. What will happen to the size of the bubble as it rises to the surface?
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
−15° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
10 atmosphere
Convert 101.325 kPa to bar.
Hot air balloons float in the air because of the low density of the air inside the balloon. Explain this with the help of an appropriate gas law.

Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
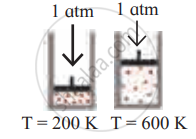 |
______________ |
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
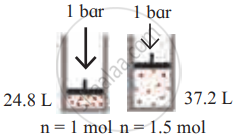 |
______________ |
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
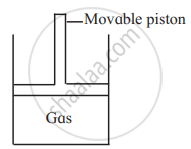
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if pressure is increased from 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar at a constant temperature.
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.

Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if the temperature is decreased from 300 K to 150 K at constant pressure.
Write the statement for Charles’ law
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, the Graph shows the relationship between pressure and volume. Represent the relation mathematically.
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Write the statement of law.
Solve the following.
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2800 m3 at 99°C. What is the volume if the air cools to 80°C?

Solve the following.
At 0°C, a gas occupies 22.4 liters. How much hot must be the gas in celsius and in kelvin to reach a volume of 25.0 liters?
Name two items that can serve as a model for Gay Lusaac’s law and explain.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
Explain the following observation.
Aerated water bottles are kept under water during summer
A sample of gas at 15°C at 1 atm. has a volume of 2.58 dm3. When the temperature is raised to 38°C at 1 atm does the volume of the gas Increase? If so, calculate the final volume.
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0°C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
A small bubble rises from the bottom of a lake where the temperature and pressure are 6°C and 4 atm. to the water surface, where the temperature is 25°C and pressure is 1 atm. Calculate the final volume in (mL) of the bubble, if its initial volume is 1.5 mL.
A gas occupies a volume of 4.2 dm3 at 101 kPa pressure. What volume will gas occupy if the pressure is increased to 235 kPa keeping the temperature constant?
10 g of gas at one atomospheric pressure is cooled from 273.15°C to 0°C keeping the volume constant. What is the final pressure?
If 300 mL of a gas at 26.85°C is cooled to 6.85°C at constant pressure. What will be the final volume of gas?
