Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a sample of a gas in a cylinder with a movable piston.
Show diagrammatically the changes in the position of the piston, if pressure is increased from 1.0 bar to 2.0 bar at a constant temperature.
उत्तर
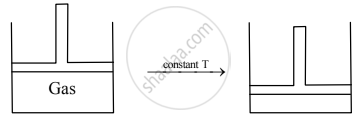
At constant T, P ∝ `1/"V"`
Since, pressure doubles, the volume will become half.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain Why?
"When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given."
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
What is meant by aqueous tension? How is the pressure exerted by a gas corrected to account for aqueous tension?
State the following:
The absolute temperature of a gas at 7°C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
273° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
1 atmosphere
Convert 89 kPa to newton per square metre (Nm−2)
Convert 101.325 kPa to bar.
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
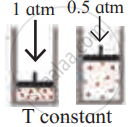 |
______________ |
Match the pairs of the following:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| a. Boyle’s law | i. at constant pressure and volume |
| b. Charles’ law | ii. at constant temperature |
| iii. at constant pressure |
Write the statement for Charles’ law
With the help of the graph answer the following -

At constant temperature, Write the statement of law.
Solve the following.
A syringe has a volume of 10.0 cm3 at pressure 1 atm. If you plug the end so that no gas can escape and push the plunger down, what must be the final volume to change the pressure to 3.5 atm?

Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is decreased by 10°C.
Solve the following.
A hot air balloon has a volume of 2800 m3 at 99°C. What is the volume if the air cools to 80°C?

The temperatures at which real gases obey the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________.
A sample of gas at 15°C at 1 atm. has a volume of 2.58 dm3. When the temperature is raised to 38°C at 1 atm does the volume of the gas Increase? If so, calculate the final volume.
Of two samples of nitrogen gas, sample A contains 1.5 moles of nitrogen in a vessel of the volume of 37.6 dm3 at 298 K, and sample B is in a vessel of volume 16.5 dm3 at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles in sample B.
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
According to Andrews isothermals, the minimum temperature at which carbon dioxide gas obeys Boyles law is ______.
According to Andrews isothermals at what temperature the carbon dioxide gas starts to condense at 73 atmosphere?
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 2 dm3 at STP. At what temperature the volume of gas becomes double, keeping the pressure constant?
At what temperature the volume of a gas becomes absolutely zero?
If 2 moles of an ideal gas at 546 K has volume of 44.8 L, then what will be it's pressure? (R = 0.082)
10 g of gas at one atomospheric pressure is cooled from 273.15°C to 0°C keeping the volume constant. What is the final pressure?
If 300 mL of a gas at 26.85°C is cooled to 6.85°C at constant pressure. What will be the final volume of gas?
