Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0°C is 2 dm3. Calculate the new volume of the gas at constant pressure when the temperature is decreased by 10°C.
उत्तर
Given:
T1 = Initial temperature = 0°C = 0 + 273.15 = 273.15 K,
V1 = Initial volume = 2 dm3
T2 = Final temperature = 273.15 K − 10 = 263.15 K
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: `"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
Calculation:
According to Charles’ law,
`"V"_1/"T"_1="V"_2/"T"_2` (at constant n and P)
∴ V2 = `("V"_1"T"_2)/"T"_1=(2xx263.15)/273.15` = 1.927 dm3
The new volume of a given mass of gas is 1.927 dm3
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State (i) the three variables for gas laws and (ii) SI units of these variables.
Give reason for the following:
Gases have a lower density compared to solids or liquids.
Give reason for the following:
Gases exert pressure in all directions.
State the following:
The absolute temperature of a gas at 7°C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
25° C
Convert the following temperature from degree Celcius to kelvin.
273° C
Convert the following pressure value into Pascals.
107000 Nm−2
Convert −100° C to kelvin
Hot air balloons float in the air because of the low density of the air inside the balloon. Explain this with the help of an appropriate gas law.

Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
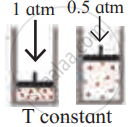 |
______________ |
Identify the gas laws from the following diagram.
| Diagram | Gas laws |
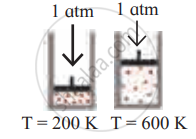 |
______________ |
Write the statement for Charles’ law
The temperatures at which real gases obey the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________.
Use of hot air balloon in sports and meteorological observation is an application of
State Boyle's law.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
Explain the following observation.
The type of an automobile is inflated to slightly lesser pressure in summer than in winter
A sample of gas at 15°C at 1 atm. has a volume of 2.58 dm3. When the temperature is raised to 38°C at 1 atm does the volume of the gas Increase? If so, calculate the final volume.
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0°C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
A small bubble rises from the bottom of a lake where the temperature and pressure are 6°C and 4 atm. to the water surface, where the temperature is 25°C and pressure is 1 atm. Calculate the final volume in (mL) of the bubble, if its initial volume is 1.5 mL.
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
According to Andrews isothermals, the minimum temperature at which carbon dioxide gas obeys Boyles law is ______.
Volume of a balloon at 25°C and 1 bar pressure is 2.27 L. If the pressure of the gas in balloon is reduced to 0.227 bar, what is the rise in volume of a gas?
According to Andrews isothermals at what temperature the carbon dioxide gas starts to condense at 73 atmosphere?
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 2 dm3 at STP. At what temperature the volume of gas becomes double, keeping the pressure constant?
At what temperature the volume of a gas becomes absolutely zero?
At what temperature, the volume of gas would become zero?
