Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define Impedance.
उत्तर
The effective opposition offered by the inductor, capacitor and resistor connected in series to flow of AC current. is called impedance.
Z = `sqrt("R"^2 + (Χ_"L" - Χ_"C")^2)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define 'quality factor' of resonance in a series LCR circuit. What is its SI unit?
In a series LCR circuit, VL = VC ≠ VR. What is the value of power factor?
Why does current in a steady state not flow in a capacitor connected across a battery? However momentary current does flow during charging or discharging of the capacitor. Explain.
A source of ac voltage v = v0 sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the condition under which watt-less current flows in the circuit ?
A series LCR circuit is connected to a source having voltage v = vm sin ωt. Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage.
Obtain the condition for resonance to occur. Define ‘power factor’. State the conditions under which it is (i) maximum and (ii) minimum.
An LR circuit having a time constant of 50 ms is connected with an ideal battery of emf ε. find the time elapsed before (a) the current reaches half its maximum value, (b) the power dissipated in heat reaches half its maximum value and (c) the magnetic field energy stored in the circuit reaches half its maximum value.
The magnetic field at a point inside a 2.0 mH inductor-coil becomes 0.80 of its maximum value in 20 µs when the inductor is joined to a battery. Find the resistance of the circuit.
An LR circuit with emf ε is connected at t = 0. (a) Find the charge Q which flows through the battery during 0 to t. (b) Calculate the work done by the battery during this period. (c) Find the heat developed during this period. (d) Find the magnetic field energy stored in the circuit at time t. (e) Verify that the results in the three parts above are consistent with energy conservation.
An inductor of inductance 2.00 H is joined in series with a resistor of resistance 200 Ω and a battery of emf 2.00 V. At t = 10 ms, find (a) the current in the circuit, (b) the power delivered by the battery, (c) the power dissipated in heating the resistor and (d) the rate at which energy is being stored in magnetic field.
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor or resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
The potential difference across the resistor is 160V and that across the inductor is 120V. Find the effective value of the applied voltage. If the effective current in the circuit be 1.0 A, calculate the total impedance of the circuit.
Answer the following question.
What is the phase difference between the voltages across the inductor and the capacitor at resonance in the LCR circuit?
Answer the following question.
Draw the diagram of a device that is used to decrease high ac voltage into a low ac voltage and state its working principle. Write four sources of energy loss in this device.
Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the current flowing in an ideal inductor connected to an a.c. source of voltage, v= vo sin ωt. Hence plot graphs showing the variation of (i) applied voltage and (ii) the current as a function of ωt.
A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 µF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Keeping the source frequency equal to the resonating frequency of the series LCR circuit, if the three elements, L, C and R are arranged in parallel, show that the total current in the parallel LCR circuit is minimum at this frequency. Obtain the current rms value in each branch of the circuit for the elements and source specified for this frequency.
In a series LCR circuit supplied with AC, ______.
In an L.C.R. series a.c. circuit, the current ______.
If an LCR series circuit is connected to an ac source, then at resonance the voltage across ______.
In an LCR series a.c. circuit, the voltage across each of the components, L, C and R is 50V. The voltage across the LC combination will be ______.
In a series LCR circuit the voltage across an inductor, capacitor and resistor are 20 V, 20 V and 40 V respectively. The phase difference between the applied voltage and the current in the circuit is ______.
At resonance frequency the impedance in series LCR circuit is ______.
The phase diffn b/w the current and voltage at resonance is
Which of the following components of an LCR circuit, with a.c. supply, dissipates energy?
A series LCR circuit containing 5.0 H inductor, 80 µF capacitor and 40 Ω resistor is connected to 230 V variable frequency ac source. The angular frequencies of the source at which power transferred to the circuit is half the power at the resonant angular frequency are likely to be ______.
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is ______.
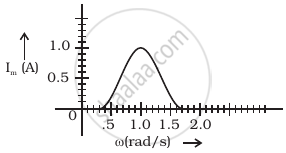
In series LCR circuit, the plot of Imax vs ω is shown in figure. Find the bandwidth and mark in the figure.
A coil of 0.01 henry inductance and 1 ohm resistance is connected to 200 volt, 50 Hz ac supply. Find the impedance of the circuit and time lag between max. alternating voltage and current.
