Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Diatomic molecules like hydrogen have energies due to both translational as well as rotational motion. From the equation in kinetic theory `pV = 2/3` E, E is ______.
- the total energy per unit volume.
- only the translational part of energy because rotational energy is very small compared to the translational energy.
- only the translational part of the energy because during collisions with the wall pressure relates to change in linear momentum.
- the translational part of the energy because rotational energies of molecules can be of either sign and its average over all the molecules is zero.
उत्तर
c
Explanation:
According to kinetic theory. we assume the walls only exert perpendicular forces on molecules. They do not exert any parallel force. hence there will not be any type of rotation present.
The wall produces one change in translational motion.
Hence, in the equation
`pV = 2/3 E` .....`[(Where P = pressure),(V = Volume)]`
E is representing only the translational part of energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The average momentum of a molecule in a sample of an ideal gas depends on
Let Q and W denote the amount of heat given to an ideal gas and the work done by it in an adiabatic process.
(a) Q = 0
(b) W = 0
(c) Q = W
(d) Q ≠ W
A vessel containing one mole of a monatomic ideal gas (molecular weight = 20 g mol−1) is moving on a floor at a speed of 50 m s−1. The vessel is stopped suddenly. Assuming that the mechanical energy lost has gone into the internal energy of the gas, find the rise in its temperature.
An amount Q of heat is added to a monatomic ideal gas in a process in which the gas performs a work Q/2 on its surrounding. Find the molar heat capacity for the process
An ideal gas (Cp / Cv = γ) is taken through a process in which the pressure and the volume vary as p = aVb. Find the value of b for which the specific heat capacity in the process is zero.
Two ideal gases have the same value of Cp / Cv = γ. What will be the value of this ratio for a mixture of the two gases in the ratio 1 : 2?
Two samples A and B, of the same gas have equal volumes and pressures. The gas in sample A is expanded isothermally to double its volume and the gas in B is expanded adiabatically to double its volume. If the work done by the gas is the same for the two cases, show that γ satisfies the equation 1 − 21−γ = (γ − 1) ln2.
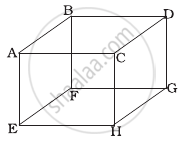
1 mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cubical volume V, ABCDEFGH at 300 K (Figure). One face of the cube (EFGH) is made up of a material which totally absorbs any gas molecule incident on it. At any given time ______.
In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature ______.
- obeys Maxwell’s distribution.
- have the same value for all molecules.
- equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule.
- is (2/3)rd the translational kinetic energy for each molecule.
The container shown in figure has two chambers, separated by a partition, of volumes V1 = 2.0 litre and V2 = 3.0 litre. The chambers contain µ1 = 4.0 and µ2 = 5.0 moles of a gas at pressures p1 = 1.00 atm and p2 = 2.00 atm. Calculate the pressure after the partition is removed and the mixture attains equilibrium.
| V1 | V2 |
| µ1, p1 | µ2 |
| p2 |
