Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a p-V diagram of the reversible process.
उत्तर
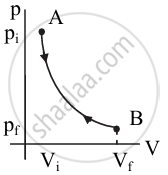
p-V diagram of reversible process
संबंधित प्रश्न
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
What is a thermodynamic process?
Draw a p-V diagram of the irreversible process.
Draw a p-V diagram showing negative work with varying pressure.
Draw a p-V diagram showing positive work at constant pressure.
Differentiate between the reversible and irreversible processes.
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Explain graphically (i) positive work with varying pressure, (ii) negative work with varying pressure, and (iii) positive work at constant pressure.
Explain the thermodynamics of the isochoric process.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
Give the equation of state for an isothermal process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
In an adiabatic expansion of the air, the volume is increased by 4%, what is the percentage change in pressure? (For air γ = 1.4)
An ideal gas is taken in a cyclic process as shown in the figure. Calculate
- work done by the gas
- work done on the gas
- Net work done in the process

For a given ideal gas 6 × 105 J heat energy is supplied and the volume of gas is increased from 4 m3 to 6 m3 at atmospheric pressure. Calculate
- the work done by the gas
- change in internal energy of the gas
- graph this process in PV and TV diagram
A monoatomic gas of pressure p having volume V expands isothermally to a volume 2V and then adiabatically to a volume 16V. The final pressure of the gas is ____________.
`("ratio of specific heats" = 5/3)`
An ideal gas is expanded isothermally from volume V1 to volume V2 and then compressed adiabatically to original volume V1. If the initial pressure is P1, the final pressure is P3 and net work done is W, then ____________.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

An ideal gas A and a real gas B have their volumes increased from V to 2V under isothermal conditions. The increase in internal energy ____________.
In an isothermal process, the volume of an ideal gas is halved. One can say that ____________.
Which of the following processes is reversible?
Give any two types of a thermodynamic process.
In the figure shown here, the work done in the process ACBA is ______.
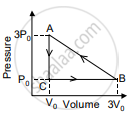
In a cyclic process, if ΔU = internal energy, W = work done, Q = Heat supplied then ______.
