Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw any circle and mark
- it's centre
- a radius
- a diameter
- a sector
- a segment
- a point in its interior
- a point in its exterior
- an arc
उत्तर
A circle is a two-dimensional figure formed by a set of points that are at a constant or at a fixed distance (radius) from a fixed point (center) in the plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In Fig. 1, PA and PB are tangents to the circle with centre O such that ∠APB = 50°. Write the measure of ∠OAB.

Two tangent segments PA and PB are drawn to a circle with center O such that ∠APB =120°. Prove that OP = 2AP
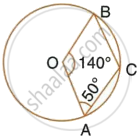
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. If ∠AOB = 140° and ∠OAC = 50°; find:
- ∠ACB,
- ∠OBC,
- ∠OAB,
- ∠CBA.
Find the length of tangent drawn to a circle with radius 8 cm form a point 17 cm away from the center of the circle
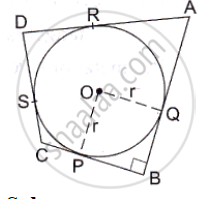
In the given figure, a circle with center O, is inscribed in a quadrilateral ABCD such that it touches the side BC, AB, AD and CD at points P, Q, R and S respectively. If AB = 29cm, AD = 23cm, ∠B = 90° and DS=5cm then find the radius of the circle.
Find the length of the chord of a circle in the following when:
Radius is 13 cm and the distance from the centre is 12 cm
The figure given below shows a circle with center O in which diameter AB bisects the chord CD at point E. If CE = ED = 8 cm and EB = 4 cm,
find the radius of the circle.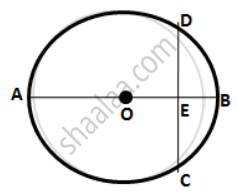
Find the area of the shaded region in the figure If ABCD is a rectangle with sides 8 cm and 6 cm and O is the centre of the circle. (Take π= 3.14)
In the figure, a circle with center P touches the semicircle at points Q and C having center O. If diameter AB = 10, AC = 6, then find the radius x of the smaller circle.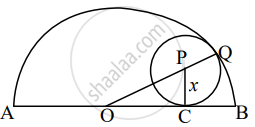
Prove that angle bisector of any angle of a triangle and perpendicular bisector of the opposite side if intersect, they will intersect on the circumcircle of the triangle.
