Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Fill the blank in the following so that the following statement is true.
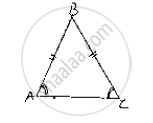
In a ΔABC if ∠A = ∠C , then AB = ......
उत्तर
In a ΔABC if , ∠A= ∠C then AB= BC
Reason: Since, the sides opposite to equal angles are equal, the side opposite to∠A
i.e., BC and ∠C i.e., AB are equal
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
ABC is a triangle in which altitudes BE and CF to sides AC and AB are equal (see the given figure). Show that
- ΔABE ≅ ΔACF
- AB = AC, i.e., ABC is an isosceles triangle.

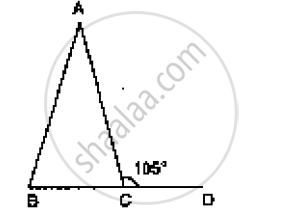
In Figure AB = AC and ∠ACD =105°, find ∠BAC.
ABC is a right angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
In a ΔPQR, if PQ = QR and L, M and N are the mid-points of the sides PQ, QR and RP
respectively. Prove that LN = MN.
Fill the blank in the following so that the following statement is true.
In an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC, if BD and CE are its altitudes, then BD is …… CE.
In a ΔABC, if ∠B = ∠C = 45°, which is the longest side?
In ΔABC, if ∠A = 40° and ∠B = 60°. Determine the longest and shortest sides of the triangle.
Write the sum of the angles of an obtuse triangle.
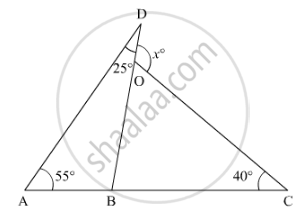
In the given figure, the value of x is ______.
ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC and D is a point on BC such that AD ⊥ BC (Figure). To prove that ∠BAD = ∠CAD, a student proceeded as follows:
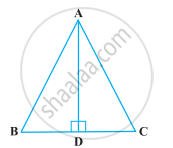
In ∆ABD and ∆ACD,
AB = AC (Given)
∠B = ∠C (Because AB = AC)
and ∠ADB = ∠ADC
Therefore, ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACD (AAS)
So, ∠BAD = ∠CAD (CPCT)
What is the defect in the above arguments?
[Hint: Recall how ∠B = ∠C is proved when AB = AC].
