Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give plausible explanation for each of the following :
Why are amines less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses?
उत्तर १
Amines undergo protonation to give amide ion.
`R- NH_2 -> R - bar(N) H + H^(+)`
Amide ion
Similarly, alcohol loses a proton to give alkoxide ion.
`R - OH -> R - bar(O) + H^(+)`
Alcohol Alkoxide ion
In an amide ion, the negative charge is on the N-atom whereas in alkoxide ion, the negative charge is on the O-atom. Since O is more electronegative than N, O can accommodate the negative charge more easily than N. As a result, the amide ion is less stable than the alkoxide ion. Hence, amines are less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses
उत्तर २
Loss of proton from an amine gives an amide ion while loss of a proton from alcohol give an alkoxide ion.
R—NH2—>R—NH– +H+
R—O —H—>R— O– +H+ .
Since O is more electronegative than N, so it wijl attract positive species more strongly in comparison to N. Thus, RO~ is more stable than RNH®. Thus, alcohols are more acidic than amines. Conversely, amines are less acidic than alcohols.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the reactions of aromatic with nitrous acid.
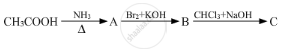
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :

Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :
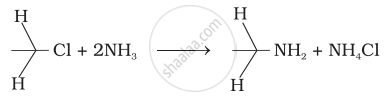
Name the process of breaking C-X bond by ammonia in preparation of amines.
Write reactions to bring about the following conversions.
Acetamide to methylamine
Write reactions for the preparation of ethanamine using Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.

Identify the major product (B).
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding Hofmann bromamide reaction.
Which of the following amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation reaction is shown by ______.
Which of the following compounds is the weakest Brönsted base?
Which of the following reactions are correct?
(i)
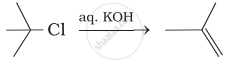
(ii)
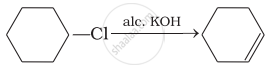
(iii)
(iv)
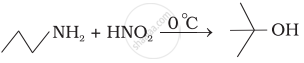
What is the best reagent to convert nitrile to primary amine?
Match the reactions given in Column I with the statements given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Ammonolysis | (a) | Amine with lesser number of carbon atoms |
| (ii) | Gabriel phthalimide synthesis | (b) | Detection test for primary amines. |
| (iii) | Hoffmann Bromamide reaction | (c) | Reaction of phthalimide with \[\ce{KOH}\] and \[\ce{R-X}\] |
| (iv) | Carbylamine reaction | (d) | Reaction of alkylhalides with \[\ce{NH3}\] |
Assertion: Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction is given by primary amines.
Reason: Primary amines are more basic than secondary amines.
What is the IUPAC name of \[\ce{(CH3)2 - N - CH3}\]?
Write the name of the product formed by the action of LiAlH4/ether on acetamide.
Write short note on the following:
Ammonolysis
Write a short note on Ammonolysis.
Assertion: Amimonolysis of alkyl halides involves the reaction between alkyl halides and alcoholic ammonia.
Reason: Ammonolysis of alkyl halides produces secondary amines only.
