Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the sum of the distances of a moving point in a plane from the axes is 1, then find the locus of the point.
उत्तर
Let coordinates of a moving point P be (x, y).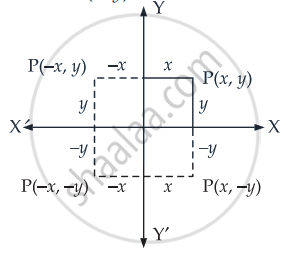
Given that the sum of the distances from the axes to the point is always 1
∴ |x| + |y| = 1
⇒ x + y = 1
⇒ – x – y = 1
⇒ – x + y = 1
⇒ x – y = 1
Hence, these equations gives us the locus of the point P which is a square.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the points on the x-axis, whose distances from the `x/3 +y/4 = 1` are 4 units.
Find the equation of the straight line at a distance of 3 units from the origin such that the perpendicular from the origin to the line makes an angle tan−1 \[\left( \frac{5}{12} \right)\] with the positive direction of x-axi .
A line a drawn through A (4, −1) parallel to the line 3x − 4y + 1 = 0. Find the coordinates of the two points on this line which are at a distance of 5 units from A.
Find the distance of the point (2, 5) from the line 3x + y + 4 = 0 measured parallel to a line having slope 3/4.
Find the distance of the point (2, 5) from the line 3x + y + 4 = 0 measured parallel to the line 3x − 4y+ 8 = 0.
Find the distance of the point (4, 5) from the straight line 3x − 5y + 7 = 0.
Find the perpendicular distance of the line joining the points (cos θ, sin θ) and (cos ϕ, sin ϕ) from the origin.
Show that the perpendiculars let fall from any point on the straight line 2x + 11y − 5 = 0 upon the two straight lines 24x + 7y = 20 and 4x − 3y − 2 = 0 are equal to each other.
Find the distance of the point of intersection of the lines 2x + 3y = 21 and 3x − 4y + 11 = 0 from the line 8x + 6y + 5 = 0.
What are the points on X-axis whose perpendicular distance from the straight line \[\frac{x}{a} + \frac{y}{b} = 1\] is a ?
If the length of the perpendicular from the point (1, 1) to the line ax − by + c = 0 be unity, show that \[\frac{1}{c} + \frac{1}{a} - \frac{1}{b} = \frac{c}{2ab}\] .
Determine the distance between the pair of parallel lines:
4x − 3y − 9 = 0 and 4x − 3y − 24 = 0
The equations of two sides of a square are 5x − 12y − 65 = 0 and 5x − 12y + 26 = 0. Find the area of the square.
Find the equation of two straight lines which are parallel to x + 7y + 2 = 0 and at unit distance from the point (1, −1).
Answer 3:
Prove that the lines 2x + 3y = 19 and 2x + 3y + 7 = 0 are equidistant from the line 2x + 3y= 6.
Write the value of θ ϵ \[\left( 0, \frac{\pi}{2} \right)\] for which area of the triangle formed by points O (0, 0), A (a cos θ, b sin θ) and B (a cos θ, − b sin θ) is maximum.
Write the locus of a point the sum of whose distances from the coordinates axes is unity.
L is a variable line such that the algebraic sum of the distances of the points (1, 1), (2, 0) and (0, 2) from the line is equal to zero. The line L will always pass through
The area of a triangle with vertices at (−4, −1), (1, 2) and (4, −3) is
The vertices of a triangle are (6, 0), (0, 6) and (6, 6). The distance between its circumcentre and centroid is
If the tangent to the curve y = 3x2 - 2x + 1 at a point Pis parallel toy = 4x + 3, the co-ordinates of P are
If P(α, β) be a point on the line 3x + y = 0 such that the point P and the point Q(1, 1) lie on either side of the line 3x = 4y + 8, then _______.
Find the points on the line x + y = 4 which lie at a unit distance from the line 4x + 3y = 10.
The distance between the lines y = mx + c1 and y = mx + c2 is ______.
The ratio in which the line 3x + 4y + 2 = 0 divides the distance between the lines 3x + 4y + 5 = 0 and 3x + 4y – 5 = 0 is ______.
