Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In ∆ABC, ∠A = ∠B = 62° ; find ∠C.
उत्तर
∠A + ∠B + ∠C= 180°
⇒ 62° + 62° + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 124° + ∠C = 180°
⇒ ∠C = 180° – 124°
⇒∠C = 56°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two angles of a triangle are equal and the third angle is greater than each of those angles
by 30°. Determine all the angles of the triangle.
ABC is a triangle in which ∠A — 72°, the internal bisectors of angles B and C meet in O.
Find the magnitude of ∠BOC.
Determine the measure of each of the equal angles of a right-angled isosceles triangle.
OR
ABC is a right-angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AB = AC. Find ∠B and ∠C.
Is the following statement true and false :
All the angles of a triangle can be greater than 60°.
In ΔABC, if bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersect at O at angle of 120°, then find the measure of ∠A.
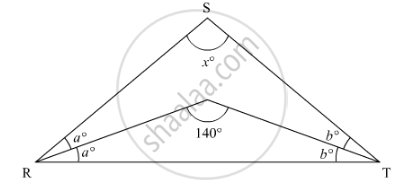
In ΔRST (See figure), what is the value of x?
The length of the three segments is given for constructing a triangle. Say whether a triangle with these sides can be drawn. Give the reason for your answer.
12 cm, 12 cm, 16 cm
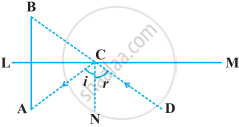
The image of an object placed at a point A before a plane mirror LM is seen at the point B by an observer at D as shown in the following figure. Prove that the image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
[Hint: CN is normal to the mirror. Also, angle of incidence = angle of reflection].
O is a point in the interior of a square ABCD such that OAB is an equilateral triangle. Show that ∆OCD is an isosceles triangle.
Which two triangles have ∠B in common?