Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In an elastic collision
विकल्प
the initial kinetic energy is equal to the final kinetic energy
the final kinetic energy is less than the initial kinetic energy
the kinetic energy remains constant
the kinetic energy first increases then decreases.
उत्तर
the initial kinetic energy is equal to the final kinetic energy
As no energy is lost into heat in an elastic collision, the initial kinetic energy is equal to the final kinetic energy.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If all the particles of a system lie in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in X-Y plane?
If all the particle of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in the cube?
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
A high-jumper successfully clears the bar. Is it possible that his centre of mass crossed the bar from below it? Try it with appropriate figures.
Consider the following the equations
(A) \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\] and
(B) \[\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{\vec{F}}{M}\]
In a noninertial frame
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
Seven homogeneous bricks, each of length L, are arranged as shown in figure. Each brick is displaced with respect to the one in contact by L/10. Find the x-coordinate fo the centre of mass relative to the origin shown.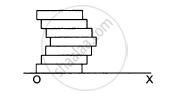
A square plate of edge d and a circular disc of diameter d are placed touching each other at the midpoint of an edge of the plate as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the combination, assuming same mass per unit area for the two plates.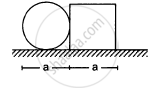
The balloon, the light rope and the monkey shown in figure are at rest in the air. If the monkey reaches the top of the rope, by what distance does the balloon descend? Mass of the balloon = M, mass of the monkey = m and the length of the rope ascended by the monkey = L.

Find the ratio of the linear momenta of two particles of masses 1.0 kg and 4.0 kg if their kinetic energies are equal.
Two fat astronauts each of mass 120 kg are travelling in a closed spaceship moving at a speed of 15 km/s in the outer space far removed from all other material objects. The total mass of the spaceship and its contents including the astronauts is 660 kg. If the astronauts do slimming exercise and thereby reduce their masses to 90 kg each, with what velocity will the spaceship move?
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
A particle of mass 100 g moving at an initial speed u collides with another particle of same mass kept initially at rest. If the total kinetic energy becomes 0.2 J after the collision, what could be the minimum and the maximum value of u.
A projectile is fired with a speed u at an angle θ above a horizontal field. The coefficient of restitution of collision between the projectile and the field is e. How far from the starting point, does the projectile makes its second collision with the field?
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
Two particles P and Q of mass 1 kg and 3 kg respectively start moving towards each other from rest under mutual attraction. What is the velocity of their center of mass?
Three equal masses each of 50 g, are placed at the corners of a right angled isosceles triangle whose two equal sides are 5 cm each. The position of the centre of mass of the system is ____________.
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with ______.
(n – 1) equal point masses each of mass m are placed at the vertices of a regular n-polygon. The vacant vertex has a position vector a with respect to the centre of the polygon. Find the position vector of centre of mass.
