Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If all the particles of a system lie in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in X-Y plane?
उत्तर
Yes, if all the particles of a system lie in the X–Y plane, then it's necessary that its centre of mass lies in the X–Y plane.
\[z_{cm} = \frac{m_1 z_1 + m_2 z_2 + . . . m_n z_n}{\sum_{} m}\]
As all the particles lie in the X–Y plane, their z-coordinates are zero.
Therefore, for the whole system, zcm = 0; i.e., its centre of mass lies in the X–Y plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If all the particle of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in the cube?
The centre of mass is defined as \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\]. Suppose we define "centre of charge" as \[\vec{R}_c = \frac{1}{Q} \sum_i q_i \vec{r_i}\] where qi represents the ith charge placed at \[\vec{r}_i\] and Q is the total charge of the system.
(a) Can the centre of charge of a two-charge system be outside the line segment joining the charges?
(b) If all the charges of a system are in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in X-Y plane?
(c) If all the charges of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in the cube?
A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the noninertial character of the frame?
Consider the following the equations
(A) \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\] and
(B) \[\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{\vec{F}}{M}\]
In a noninertial frame
A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with the walls. The box is kept on a smooth surface. The velocity of the centre of mass
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
A car of mass M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a pendulum bob of mass m hangs from the roof of the cart. The string breaks, the bob falls on the floor, makes serval collisions on the floor and finally lands up in a small slot made in the floor. The horizontal distance between the string and the slot is L. Find the displacement of the cart during this process.
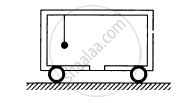
The balloon, the light rope and the monkey shown in figure are at rest in the air. If the monkey reaches the top of the rope, by what distance does the balloon descend? Mass of the balloon = M, mass of the monkey = m and the length of the rope ascended by the monkey = L.

In an elastic collision
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
Consider a gravity-free hall in which an experimenter of mass 50 kg is resting on a 5 kg pillow, 8 ft above the floor of the hall. He pushes the pillow down so that it starts falling at a speed of 8 ft/s. The pillow makes a perfectly elastic collision with the floor, rebounds and reaches the experimenter's head. Find the time elapsed in the process.
The radius and mass of earth are increased by 0.5%. Which of the following statements are true at the surface of the earth?
A shell of mass 'M' initially at rest suddenly explodes in three fragments. Two of these fragments are of mass 'M/4' each, which move with velocities 3 ms-1 and 4 ms-1 respectively in mutually perpendicular directions. The magnitude of velocity of the third fragment is ______.
Centre of mass is a point ______.
Separation of Motion of a system of particles into motion of the centre of mass and motion about the centre of mass:
- Show pi = p’i + miV Where pi is the momentum of the ith particle (of mass mi) and p′ i = mi v′ i. Note v′ i is the velocity of the ith particle relative to the centre of mass. Also, prove using the definition of the centre of mass `sum"p""'"_"t" = 0`
-
Show K = K′ + 1/2MV2
where K is the total kinetic energy of the system of particles, K′ is the total kinetic energy of the
system when the particle velocities are taken with respect to the centre of mass and MV2/2 is the
kinetic energy of the translation of the system as a whole (i.e. of the centre of mass motion of the
system). The result has been used in Sec. 7.14. - Show where `"L""'" = sum"r""'"_"t" xx "p""'"_"t"` is the angular momentum of the system about the centre of mass with
velocities taken relative to the centre of mass. Remember `"r"_"t" = "r"_"t" - "R"`; rest of the notation is the standard notation used in the chapter. Note L′ and MR × V can be said to be angular momenta, respectively, about and of the centre of mass of the system of particles. - Show `"dL"^"'"/"dt" = ∑"r"_"i"^"'" xx "dP"^"'"/"dt"`
Further show that `"dL"^'/"dt" = τ_"ext"^"'"`
Where `"τ"_"ext"^"'"` is the sum of all external torques acting on the system about the centre of mass.
(Hint: Use the definition of centre of mass and third law of motion. Assume the internal forces between any two particles act along the line joining the particles.)
Which of the following statements are correct?
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?
The mass per unit length of a non-uniform rod of length L varies as m = λx where λ is constant. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
