Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The centre of mass is defined as \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\]. Suppose we define "centre of charge" as \[\vec{R}_c = \frac{1}{Q} \sum_i q_i \vec{r_i}\] where qi represents the ith charge placed at \[\vec{r}_i\] and Q is the total charge of the system.
(a) Can the centre of charge of a two-charge system be outside the line segment joining the charges?
(b) If all the charges of a system are in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in X-Y plane?
(c) If all the charges of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in the cube?
उत्तर
(a) Yes
Consider a charge distributed in X-Y plane.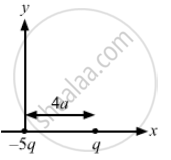
\[X_{cm} = \frac{- 6q \times 0 + q \times 5a}{- 6q + q} = - a\]
(b) Yes. Because the z-coordinates of all the charges are zero, the centre of charge lies in X-Y plane.
(c) No, it is not necessary that the centre of charge lies in the cube because charge can be either negative or positive.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the location of the centre of mass of a
- sphere,
- cylinder,
- ring, and
- cube,
each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
If all the particle of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of mass be in the cube?
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
If the external force acting on a system have zero resultant, the centre of mass
(a) must not move
(b) must not accelerate
(c) may move
(d) may accelerate.
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
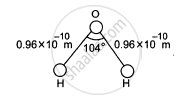
The structure of a water molecule is shown in figure. Find the distance of the centre of mass of the molecule from the centre of the oxygen atom.
A projectile is fired with a speed u at an angle θ above a horizontal field. The coefficient of restitution of collision between the projectile and the field is e. How far from the starting point, does the projectile makes its second collision with the field?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the block of mass m1 is pulled by a constant force F1 and the other block is pulled by a constant force F2. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
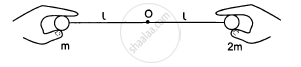
Two balls having masses m and 2m are fastened to two light strings of same length l (See figure). The other ends of the strings are fixed at O. The strings are kept in the same horizontal line and the system is released from rest. The collision between the balls is elastic. (a) Find the velocity of the balls just after their collision. (b) How high will the ball rise after the collision?
Solve the following problem.
Four uniform solid cubes of edges 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm are kept on the ground, touching each other in order. Locate centre of mass of their system.
A round object of mass M and radius R rolls down without slipping along an inclined plane. The frictional force, ______
Two particles P and Q of mass 1 kg and 3 kg respectively start moving towards each other from rest under mutual attraction. What is the velocity of their center of mass?
A body of mass 2 kg is acted upon by two forces each of magnitude 1 N and inclined at 60° with each other. The acceleration of the body in m/s is ____________. [cos 60° = 0.5]
Which of the following has maximum momentum?
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with ______.
Which of the following statements are correct?
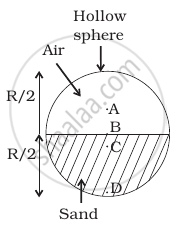
Which of the following points is the likely position of the centre of mass of the system shown in figure?
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
