Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
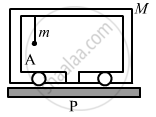
A car of mass M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a pendulum bob of mass m hangs from the roof of the cart. The string breaks, the bob falls on the floor, makes serval collisions on the floor and finally lands up in a small slot made in the floor. The horizontal distance between the string and the slot is L. Find the displacement of the cart during this process.
उत्तर
The mass of the bob is m.
The mass of the cart is M.
Considering the bob falls at point A.
Initial distance of centre of mass of the system from P is given as
\[x = \frac{m \times L + M \times 0}{M + m} = \frac{m}{M + m}L\]
When the bob falls in the slot, the distance of centre of mass of the system from P becomes zero.
\[\therefore \text{ Shift in centre of mass } = 0 - \frac{mL}{M + m}\]
\[ = - \frac{mL}{M + m} \text{ towards left}\]
\[ = \frac{mL}{M + m} \text{ towards right}\]
Therefore, the cart moves a distance of
\[\frac{mL}{M + m}\] towards right.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the location of the centre of mass of a
- sphere,
- cylinder,
- ring, and
- cube,
each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10–10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
The centre of mass is defined as \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\]. Suppose we define "centre of charge" as \[\vec{R}_c = \frac{1}{Q} \sum_i q_i \vec{r_i}\] where qi represents the ith charge placed at \[\vec{r}_i\] and Q is the total charge of the system.
(a) Can the centre of charge of a two-charge system be outside the line segment joining the charges?
(b) If all the charges of a system are in X-Y plane, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in X-Y plane?
(c) If all the charges of a system lie in a cube, is it necessary that the centre of charge be in the cube?
You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
Consider the following the equations
(A) \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\] and
(B) \[\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{\vec{F}}{M}\]
In a noninertial frame
Consider a system of two identical particles. One of the particles is at rest and the other has an acceleration a. The centre of mass has an Acceleration
In an elastic collision
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
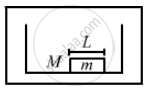
Consider a gravity-free hall in which a tray of mass M, carrying a cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L, is at rest in the middle. If the ice melts, by what distance does the centre of mass of "the tray plus the ice" system descend?
A ball of mass m is dropped onto a floor from a certain height. The collision is perfectly elastic and the ball rebounds to the same height and again falls. Find the average force exerted by the ball on the floor during a long time interval.
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose each of the blocks is pulled by a constant force F instead of any impulse. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer and the distance moved by the two blocks in the process.
Consider a gravity-free hall in which an experimenter of mass 50 kg is resting on a 5 kg pillow, 8 ft above the floor of the hall. He pushes the pillow down so that it starts falling at a speed of 8 ft/s. The pillow makes a perfectly elastic collision with the floor, rebounds and reaches the experimenter's head. Find the time elapsed in the process.
The centre of mass of a system of two particles divides the distance between them ______.
A bullet of mass 20 gram is fired from a gun of mass 2.5 kg with a speed of 750 m/s. The magnitude of recoil velocity of the gun is ______.
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with ______.
Find the centre of mass of a uniform (a) half-disc, (b) quarter-disc.
The mass per unit length of a non-uniform rod of length L varies as m = λx where λ is constant. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
