Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न

In Figure 1, PS = 3 cm, QS = 4 cm, ∠PRQ = θ, ∠PSQ = 90°, PQ ⊥ RQ and RQ = 9 cm. Evaluate tan θ.
उत्तर
Given,
PS = 3 cm, QS = 4 cm, RQ = 9cm
In In ΔPSQ,
PQ2 =PS2 + OS2
PQ2 = 32 +42 = 25
⇒ PQ = 5 cm
In Δ PQR,
tan θ =`"PQ"/"RQ"`
⇒ tan θ =`5/9`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
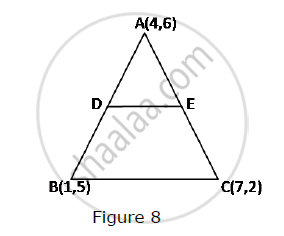
In Fig. 8, the vertices of ΔABC are A(4, 6), B(1, 5) and C(7, 2). A line-segment DE is drawn to intersect the sides AB and AC at D and E respectively such that `(AD)/(AB)=(AE)/(AC)=1/3 `Calculate th area of ADE and compare it with area of ΔABCe.
For what value of k are the points (k, 2 – 2k), (–k + 1, 2k) and (–4 – k, 6 – 2k) are collinear ?
Determine the ratio in which the line 2x + y – 4 = 0 divides the line segment joining the points A(2, – 2) and B(3, 7).
The two opposite vertices of a square are (− 1, 2) and (3, 2). Find the coordinates of the other two vertices.
Find equation of line joining (3, 1) and (9, 3) using determinant.
For what value of a point (a, 1), (1, -1) and (11, 4) are collinear?
Prove that the lines joining the middle points of the opposite sides of a quadrilateral and the join of the middle points of its diagonals meet in a point and bisect one another
In ☐ABCD, l(AB) = 13 cm, l(DC) = 9 cm, l(AD) = 8 cm, find the area of ☐ABCD.
The area of a triangle with vertices A, B, C is given by ______.
Find the missing value:
| Base | Height | Area of Triangle |
| ______ | 31.4 mm | 1256 mm2 |
