Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a p-n junction,
(a) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material
(b) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region
(c) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material
(d) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region.
उत्तर
(a) new holes and conduction electrons are produced continuously throughout the material
(d) holes and conduction electrons recombine continuously throughout the material except in the depletion region
In a p‒n junction diode, diffusion current flows because of the diffusion of holes from the p side to the n side and of electrons from the n side to the p side. The current flowing in the diode due to the diffusion of charge carriers across the junction is called the diffusion current. The current flowing in the diode due to the movement of minority carriers across the junction due to their thermal energy is called the drift current. In an unbiased diode, the net current flowing across the junction is zero due to the cancellation of the drift current by the diffusion current. For the flow of diffusion and drift currents, holes and electrons are produced continuously throughout the material. When a hole crosses the junction, it combines with an electron on the n side. As the depletion region is devoid of free charge carriers, this recombination never takes place inside the depletion region.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In an unbiased p-n junction, holes diffuse from the p-region to n-region because ______.
Write the two processes that take place in the formation of a p-n junction.
A student wants to use two p-n junction diodes to convert alternating current into direct current. Draw the labelled circuit diagram she would use and explain how it works.
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of a photo-diode. Write briefly how it is used to detect the optical signals.
Explain, with the help of a circuit diagram, the working of n-p-n transistor as a common emitter amplifier.
How is a zener diode fabricated so as to make it a special purpose diode? Draw I-V characteristics of zener diode and explain the significance of breakdown voltage.
Explain briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a p-n junction diode works as a half wave rectifier.
The drift current in a reverse-biased p-n junction is increased in magnitude if the temperature of the junction is increased. Explain this on the basis of creation of hole-electron pairs.
If the two ends of a p-n junction are joined by a wire,
The drift current in a p-n junction is
Diffusion current in a p-n junction is greater than the drift current in magnitude
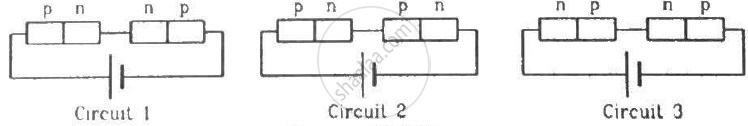
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
A semiconducting device is connected in a series circuit with a battery and a resistance. A current is found to pass through the circuit. If the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current drops to almost zero. the device may be
(a) an intrinsic semiconductor
(b) a p-type semiconductor
(c) an n-type semiconductor
(d) a p-n junction
The potential barrier existing across an unbiased p-n junction is 0.2 volt. What minimum kinetic energy a hole should have to diffuse from the p-side to the n-side if (a) the junction is unbiased, (b) the junction is forward-biased at 0.1 volt and (c) the junction is reverse-biased at 0.1 volt?
Consider a p-n junction diode having the characteristic \[i - i_0 ( e^{eV/kT} - 1) \text{ where } i_0 = 20\mu A\] . The diode is operated at T = 300 K . (a) Find the current through the diode when a voltage of 300 mV is applied across it in forward bias. (b) At what voltage does the current double?
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30µA to 80µA, the collector current is changed from 1.0 mA to 3.5 mA. Find the current gain β.
A diode, a resistor and a 50 Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulses per second through the resistor is __________ .
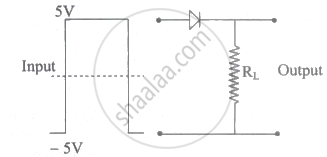
If in a p-n junction diode, a square input signal of 10 V is applied as shown Then the output signal across RL will be ______