Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
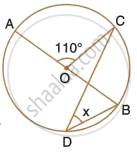
In the figure, given alongside, AOB is a diameter of the circle and ∠AOC = 110°. Find ∠BDC.
उत्तर

Join AD.
Here, `∠ADC = 1/2 ∠AOC`
= `1/2xx 110^circ`
= 55°
(Angle at the centre is double the angle at the circumference subtended by the same chord)
Also, ∠ADB = 90°
(Angle in a semicircle is a right angle)
∴ ∠BDC = 90° – ∠ADC
= 90° – 55°
= 35°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
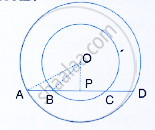
In the following figure, AD is a straight line. OP ⊥ AD and O is the centre of both the circles. If OA = 34 cm. OB = 20 cm and OP = 16cm; find the length of AB.
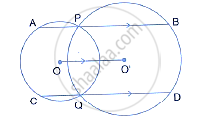
In the following figure; P and Q are the points of intersection of two circles with centres O and O’. If straight lines APB and CQD are parallel to O O'; prove that:
(i) O O' = `1/2AB` (ii) AB = CD
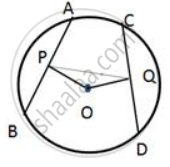
In the figure, AB is common chord of the two circles. If AC and AD are diameters; prove that D, B and C are in a straight line. O1 and O2 are the centers of two circles.

In the figure, AB is the chord of a circle with centre O and DOC is a line segment such that BC = DO. If ∠C = 20°, find angle AOD.

In the given figure, QAP is the tangent at point A and PBD is a straight line.
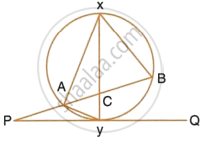
If ∠ACB = 36° and ∠APB = 42°, find:
- ∠BAP
- ∠ABD
- ∠QAD
- ∠BCD
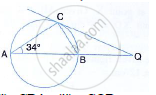
In the given figure, AB is the diameter. The tangent at C meets AB produced at Q.
If ∠CAB = 34°, Find : ∠CBA
Two circles are drawn with sides AB, AC of a triangle ABC as diameters. They intersect at a point D. Prove that D lies on BC.
Prove that the circle drawn on any one of the equal sides of an isosceles triangle as diameter bisects the base.
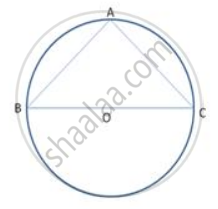
In following figure . O is the centre of the circle. Find ∠ BAC.
In the given figure, AB and CD are two equal chords of a circle, with centre O. If P is the mid-point of chord AB, Q is the mid-point of chord CD and ∠POQ = 150°, find ∠APQ.