Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In two concentric circles, a chord of length 8 cm of the large circle touches the smaller circle. If the radius of the larger circle is 5 cm, then find the radius of the smaller circle.
उत्तर
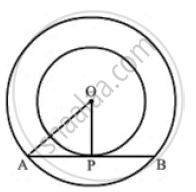
We know that the radius and tangent are perpendicular at their point of contact since the perpendicular drawn from the centre bisects the chord.
∴ AP = PB = `(AB)/2` = 4 cm
In the right triangle, AOP
AO2 = OP2 + PA2
⇒ 52 = OP2 + 42
⇒ OP2 = 9
⇒ OP = 3 cm
Hence, the radius of the smaller circle is 3 cm.
संबंधित प्रश्न
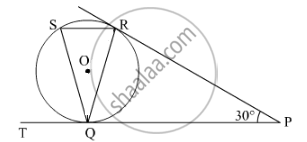
In the given figure, tangents PQ and PR are drawn from an external point P to a circle with centre O, such that ∠RPQ = 30°. A chord RS is drawn parallel to the tangent PQ. Find ∠RQS.
In the given figure, PQ and RS are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersects PQ at A and RS at B. Prove that ∠AOB = 90º
In figure PA and PB are tangents from an external point P to the circle with centre O. LN touches the circle at M. Prove that PL + LM = PN + MN
The perimeter (in cm) of a square circumscribing a circle of radius a cm, is
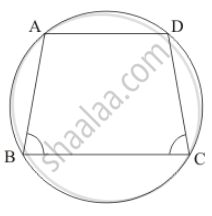
If ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral in which AD || BC (In the given figure). Prove that ∠B = ∠C.
Use the figure given below to fill in the blank:
EF is a ______ of the circle.
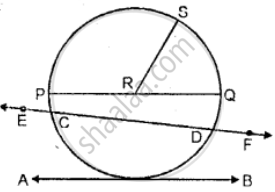
A part of circumference of a circle is called as _______
Given: A circle inscribed in a right angled ΔABC. If ∠ACB = 90° and the radius of the circle is r.
To prove: 2r = a + b – c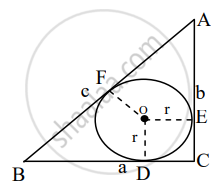
In a right triangle ABC in which ∠B = 90°, a circle is drawn with AB as diameter intersecting the hypotenuse AC and P. Prove that the tangent to the circle at P bisects BC.
In the given figure, O is the centre of the circle. Name a chord, which is not the diameter of the circle.