Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
उत्तर
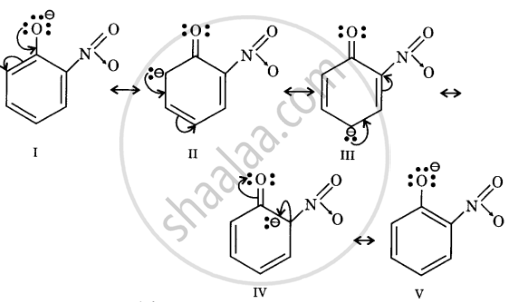
Resonance structures of o-nitrophenoxide ion
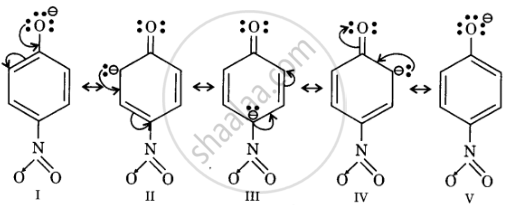
Resonance structures of p-nitrophenoxide ion
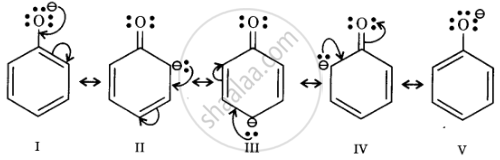
Resonance structures of phenoxide ion
In substituted phenols, electron withdrawing groups such as nitro group increase the acidic strength of phenol. This effect becomes more potent when such groups are present at ortho and para positions. This is because of the effective delocalisation of the anion of the phenoxide ion. Hence, o- and p-nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Oxidation of propan-1-ol with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Dilute HNO3 with phenol.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
Lucas reagent is ____________.
Lucas test is used for the detection of _____________.
The compound which reacts fastest with Lucas reagent at room temperature is:
In the reduction \[\ce{R - CHO + H2 -> RCH2OH}\] the catalyst used is:
Dehydration of 2-butanol yields:
Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone?
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
Identify the secondary alcohols from the following set:
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3}\]
- \[\ce{(C2H5)3COH}\]
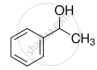
Explain why nucleophilic substitution reactions are not very common in phenols.
The correct geometry around oxygen in CH3OCH3 is
What happens when (CH3)3 C – OH is heated with Cu/573 K?
Write the chemical equation in support of your answer.
Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation?
Which of the following observation is shown by 2-phenyl ethanol with Lucas Reagent?
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
