Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove that: If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, then it is a rhombus.
उत्तर
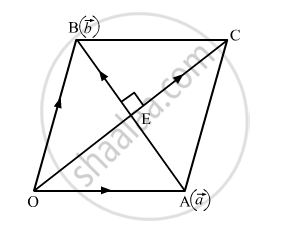
Let OACB be a quadrilateral such that diagonals OC and AB bisect each other at 90º.
Taking O as the origin, let the poisition vectors of A and B be \[\vec{a}\] and \[\vec{b}\] respectively.
Then, \[\vec{OA} = \vec{a}\] and \[\vec{OB} = \vec{b}\] Position vector of mid-point of AB, \[\vec{OE} = \frac{\vec{a} + \vec{b}}{2}\]
∴ Position vector of C, \[\vec{OC} = \vec{a} + \vec{b}\]
By the triangle law of vector addition, we have
\[\vec{OA} + \vec{AB} = \vec{OB} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec{AB} = \vec{OB} - \vec{OA} = \vec{b} - \vec{a}\]
Since \[\vec{AB} \perp \vec{OC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \vec{AB} . \vec{OC} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \vec{b} - \vec{a} \right) . \left( \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 - \left| \vec{a} \right|^2 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{a} \right|^2 = \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{a} \right| = \left| \vec{b} \right|\]
\[ \Rightarrow OA = OB\]
In a quadrilateral if diagonals bisects each other at right angle and adjacent sides are equal, then it is a rhombus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the coordinate of the point P where the line through A(3, –4, –5) and B(2, –3, 1) crosses the plane passing through three points L(2, 2, 1), M(3, 0, 1) and N(4, –1, 0).
Also, find the ratio in which P divides the line segment AB.
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q whose position vectors are `P(2veca + vecb)` and `Q(veca - 3vecb)` externally in the ratio 1: 2. Also, show that P is the mid point of the line segment RQ.
(Pythagoras's Theorem) Prove by vector method that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular if and only if the rectangle is a square.
If the median to the base of a triangle is perpendicular to the base, then triangle is isosceles.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, prove that \[{AB}^2 + {BC}^2 + {CD}^2 + {DA}^2 = {AC}^2 + {BD}^2 + 4 {PQ}^2\] where P and Q are middle points of diagonals AC and BD.
If the points A(3, 0, p), B(–1, q, 3) and C(–3, 3, 0) are collinear, then find
- the ratio in which the point C divides the line segment AB
- the values of p and q.
In Δ OAB, E is the midpoint of OB and D is the point on AB such that AD : DB = 2 : 1. If OD and AE intersect at P, then determine the ratio OP : PD using vector methods.
Find the volume of a parallelopiped whose coterimus edges are represented by the vectors `hat"i" + hat"k", hat"i" + hat"k", hat"i" + hat"j"`. Also find volume of tetrahedron having these coterminus edges.
Prove that medians of a triangle are concurrent
Prove that altitudes of a triangle are concurrent
If the plane 2x + 3y + 5z = 1 intersects the co-ordinate axes at the points A, B, C, then the centroid of Δ ABC is ______.
If P(2, 2), Q(- 2, 4) and R(3, 4) are the vertices of Δ PQR then the equation of the median through vertex R is ______.
If the position vectors of points A and B are `hati + 8hatj + 4hatk` and `7hati + 2hatj - 8hatk`, then what will be the position vector of the midpoint of AB?
If G and G' are the centroids of the triangles ABC and A'B'C', then `overline("A""A"^') + overline("B""B"^') + overline("C""C"^')` is equal to ______
If the orthocentre and circumcentre of a triangle are (-3, 5, 1) and (6, 2, -2) respectively, then its centroid is ______
If G`(overlineg)` is the centroid, `H(overlineh)` is the orthocentre and P`(overlinep)` is the circumcentre of a triangle and `xoverlinep + yoverlineh + zoverlineg = 0`, then ______
If A, B, C are the vertices of a triangle whose position vectors are `overline("a"),overline("b"),overline("c")` and G is the centroid of the `triangle ABC,` then `overline("GA")+overline("GB")+overline("GC")` is ______.
The co-ordinates of the points which divides line segment joining the point A(2, –6, 8) and B(–1, 3,–4) internally in the ratio 1: 3' are ______.
Let `square`PQRS be a quadrilateral. If M and N are midpoints of the sides PQ and RS respectively then `bar"PS" + bar"OR"` = ______.
In ΔABC, P is the midpoint of BC, Q divides CA internally in the ratio 2:1 and R divides AB externally in the ratio 1:2, then ______.
Find the unit vector in the diret:tion of the vector `veca = hati + hatj + 2hatk`
If D, E, F are the mid points of the sides BC, CA and AB respectively of a triangle ABC and 'O' is any point, then, `|vec(AD) + vec(BE) + vec(CF)|`, is ______.
In ΔABC the mid-point of the sides AB, BC and CA are respectively (l, 0, 0), (0, m, 0) and (0, 0, n). Then, `("AB"^2 + "BC"^2 + "CA"^2)/("l"^2 + "m"^2 + "n"^2)` is equal to ______.
ΔABC has vertices at A = (2, 3, 5), B = (–1, 3, 2) and C = (λ, 5, µ). If the median through A is equally inclined to the axes, then the values of λ and µ respectively are ______.
If `overlinea, overlineb, overlinec` are the position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively and `5overlinea + 3overlineb - 8overlinec = overline0` then find the ratio in which the point C divides the line segment AB.
The position vectors of three consecutive vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are `A(4hati + 2hatj - 6hatk), B(5hati - 3hatj + hatk)`, and `C(12hati + 4hatj + 5hatk)`. The position vector of D is given by ______.
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara +2barb ` and `bara-3barb `.If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is `3bara-barb` .
If `bara, barb` and `barr` are position vectors of the points A, B and R respectively and R divides the line segment AB externally in the ratio m : n, then prove that `barr = (mbarb - nbara)/(m - n)`.
Find the ratio in which the point C divides segment AB, if `5bara + 4barb - 9barc = bar0`
If `bara, barb, barc` are the position vectors of the points A, B, C respectively and `5 bar a - 3 bar b - 2 bar c = bar 0`, then find the ratio in which the point C divides the line segment BA.
The position vector of points A and B are `6 bara + 2 barb and bara - 3 barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is `3 bara - barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are 6`bara + 2barb and bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is 3`bara - barb`.
The position vectors of points A and B are 6`bara` + 2`barb` and `bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3:2, then show that the position vector of C is 3`bara - b`.
