Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Prove that: If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, then it is a rhombus.
उत्तर
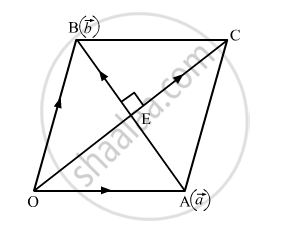
Let OACB be a quadrilateral such that diagonals OC and AB bisect each other at 90º.
Taking O as the origin, let the poisition vectors of A and B be \[\vec{a}\] and \[\vec{b}\] respectively.
Then, \[\vec{OA} = \vec{a}\] and \[\vec{OB} = \vec{b}\] Position vector of mid-point of AB, \[\vec{OE} = \frac{\vec{a} + \vec{b}}{2}\]
∴ Position vector of C, \[\vec{OC} = \vec{a} + \vec{b}\]
By the triangle law of vector addition, we have
\[\vec{OA} + \vec{AB} = \vec{OB} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \vec{AB} = \vec{OB} - \vec{OA} = \vec{b} - \vec{a}\]
Since \[\vec{AB} \perp \vec{OC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \vec{AB} . \vec{OC} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( \vec{b} - \vec{a} \right) . \left( \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right) = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 - \left| \vec{a} \right|^2 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{a} \right|^2 = \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \left| \vec{a} \right| = \left| \vec{b} \right|\]
\[ \Rightarrow OA = OB\]
In a quadrilateral if diagonals bisects each other at right angle and adjacent sides are equal, then it is a rhombus.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
By vector method prove that the medians of a triangle are concurrent.
Prove by vector method that the sum of the squares of the diagonals of a parallelogram is equal to the sum of the squares of its sides.
Prove that the diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular if and only if the rectangle is a square.
Find the position vector of point R which divides the line joining the points P and Q whose position vectors are `2hati - hatj + 3hatk` and `- 5hati + 2hatj - 5hatk` in the ratio 3:2 is internally.
Find the position vector of midpoint M joining the points L(7, –6, 12) and N(5, 4, –2).
The position vector of points A and B are `6bar"a" + 2bar"b"` and `bar"a" - 3bar"b"`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2, show that the position vector of C is `3bar"a" - bar"b"`.
Prove that the line segments joining the midpoints of the adjacent sides of a quadrilateral form a parallelogram.
If the centroid of a tetrahedron OABC is (1, 2, - 1) where A(a, 2, 3), B(1, b, 2), C(2, 1, c), find the distance of P(a, b, c) from origin.
The points A, B, C have position vectors `bar"a", bar"b" and bar"c"` respectively. The point P is the midpoint of AB. Find the vector `bar"PC"` in terms of `bar"a", bar"b", bar"c"`.
If D, E, F are the midpoints of the sides BC, CA, AB of a triangle ABC, prove that `bar"AD" + bar"BE" + bar"CF" = bar0`.
Find the position vector of point R which divides the line joining the points P and Q whose position vectors are `2hat"i" - hat"j" + 3hat"k"` and `-5hat"i" + 2hat"j" - 5hat"k"` in the ratio 3:2
(i) internally
(ii) externally
If A(5, 1, p), B(1, q, p) and C(1, −2, 3) are vertices of triangle and `"G"("r", -4/3, 1/3)` is its centroid then find the values of p, q and r
Prove that altitudes of a triangle are concurrent
If A(1, 3, 2), B(a, b, - 4) and C(5, 1, c) are the vertices of triangle ABC and G(3, b, c) is its centroid, then
If G(3, -5, r) is centroid of triangle ABC where A(7, - 8, 1), B(p, q, 5) and C(q + 1, 5p, 0) are vertices of a triangle then values of p, q, rare respectively.
P is the point of intersection of the diagonals of the parallelogram ABCD. If O is any point, then `overline"OA" + overline"OB" + overline"OC" + overline"OD"` = ______
If P(2, 2), Q(- 2, 4) and R(3, 4) are the vertices of Δ PQR then the equation of the median through vertex R is ______.
If G and G' are the centroids of the triangles ABC and A'B'C', then `overline("A""A"^') + overline("B""B"^') + overline("C""C"^')` is equal to ______
If M and N are the midpoints of the sides BC and CD respectively of a parallelogram ABCD, then `overline(AM) + overline(AN)` = ______
The co-ordinates of the points which divides line segment joining the point A(2, –6, 8) and B(–1, 3,–4) internally in the ratio 1: 3' are ______.
In ΔABC, P is the midpoint of BC, Q divides CA internally in the ratio 2:1 and R divides AB externally in the ratio 1:2, then ______.
Find the unit vector in the diret:tion of the vector `veca = hati + hatj + 2hatk`
In ΔABC the mid-point of the sides AB, BC and CA are respectively (l, 0, 0), (0, m, 0) and (0, 0, n). Then, `("AB"^2 + "BC"^2 + "CA"^2)/("l"^2 + "m"^2 + "n"^2)` is equal to ______.
ΔABC has vertices at A = (2, 3, 5), B = (–1, 3, 2) and C = (λ, 5, µ). If the median through A is equally inclined to the axes, then the values of λ and µ respectively are ______.
Using vector method, prove that the perpendicular bisectors of sides of a triangle are concurrent.
AB and CD are two chords of a circle intersecting at right angles to each other at P. If R is the centre of the circle, prove that:
`bar(PA) + bar(PB) + bar(PC) + bar(PD) = 2bar(PR)`
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara + 2 barb and bara - 3 barb`. If point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2, then show that the position vector of C is `3bara - barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara + 2 barb` and `bara-3 barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is `3bara -barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara + 2barb` and `bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2, then show that the position vector of C is `3bara - barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are `6 bara + 2 barb and bara - 3 barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is `3 bara - barb`.
The position vectors of points A and B are 6`bara` + 2`barb` and `bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3:2, then show that the position vector of C is 3`bara - b`.
