Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(Pythagoras's Theorem) Prove by vector method that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
उत्तर
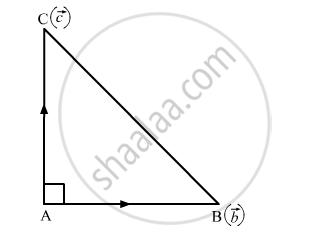
Let ABC be a right triangle with \[\angle\]BAC = 90º. Taking A as the origin, let the position vectors of B and C be \[\vec{b}\] and \[\vec{c}\] respectively. Then, \[\vec{AB} = \vec{b}\] and \[\vec{AC} = \vec{c}\]
Since \[\vec{AB} \perp \vec{AC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \vec{b} . \vec{c} = 0\] ...........................(1)
Now
\[\left| \vec{AB} \right|^2 + \left| \vec{AC} \right|^2 = \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 + \left| \vec{c} \right|^2\] , ........................(2)
Also,
\[\left| \vec{BC} \right|^2 = \left| \vec{c} - \vec{b} \right|^2 \]
\[ = \left( \vec{c} - \vec{b} \right) . \left( \vec{c} - \vec{b} \right)\]
\[ = \left| \vec{c} \right|^2 - 2 \vec{b} . \vec{c} + \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 \]
\[ = \left| \vec{c} \right|^2 + \left| \vec{b} \right|^2 . . . . . \left( 3 \right) ........................\left[ \text{ Using }] \left( 1 \right) \right]\]
From (2) and (3), we have
\[\left| \vec{AB} \right|^2 + \left| \vec{AC} \right|^2 = \left| \vec{BC} \right|^2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
By vector method prove that the medians of a triangle are concurrent.
Show that the points A (1, –2, –8), B (5, 0, –2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC.
Prove that: If the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, then it is a rhombus.
Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle are perpendicular if and only if the rectangle is a square.
If AD is the median of ∆ABC, using vectors, prove that \[{AB}^2 + {AC}^2 = 2\left( {AD}^2 + {CD}^2 \right)\]
If the median to the base of a triangle is perpendicular to the base, then triangle is isosceles.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, prove that \[{AB}^2 + {BC}^2 + {CD}^2 + {DA}^2 = {AC}^2 + {BD}^2 + 4 {PQ}^2\] where P and Q are middle points of diagonals AC and BD.
Let `A (bara)` and `B (barb)` are any two points in the space and `"R"(bar"r")` be a point on the line segment AB dividing it internally in the ratio m : n, then prove that `bar r = (mbarb + nbara)/(m + n) `
The position vector of points A and B are `6bar"a" + 2bar"b"` and `bar"a" - 3bar"b"`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2, show that the position vector of C is `3bar"a" - bar"b"`.
Prove that the line segments joining the midpoints of the adjacent sides of a quadrilateral form a parallelogram.
Prove that the median of a trapezium is parallel to the parallel sides of the trapezium and its length is half of the sum of the lengths of the parallel sides.
In Δ OAB, E is the midpoint of OB and D is the point on AB such that AD : DB = 2 : 1. If OD and AE intersect at P, then determine the ratio OP : PD using vector methods.
Prove that `(bar"a" xx bar"b").(bar"c" xx bar"d")` =
`|bar"a".bar"c" bar"b".bar"c"|`
`|bar"a".bar"d" bar"b".bar"d"|.`
Find the position vector of point R which divides the line joining the points P and Q whose position vectors are `2hat"i" - hat"j" + 3hat"k"` and `-5hat"i" + 2hat"j" - 5hat"k"` in the ratio 3:2
(i) internally
(ii) externally
If G(a, 2, −1) is the centroid of the triangle with vertices P(1, 2, 3), Q(3, b, −4) and R(5, 1, c) then find the values of a, b and c
Prove that medians of a triangle are concurrent
Prove that altitudes of a triangle are concurrent
Prove that the angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent
If the plane 2x + 3y + 5z = 1 intersects the co-ordinate axes at the points A, B, C, then the centroid of Δ ABC is ______.
P is the point of intersection of the diagonals of the parallelogram ABCD. If O is any point, then `overline"OA" + overline"OB" + overline"OC" + overline"OD"` = ______
If M and N are the midpoints of the sides BC and CD respectively of a parallelogram ABCD, then `overline(AM) + overline(AN)` = ______
If G`(overlineg)` is the centroid, `H(overlineh)` is the orthocentre and P`(overlinep)` is the circumcentre of a triangle and `xoverlinep + yoverlineh + zoverlineg = 0`, then ______
If `3bar"a" + 5bar"b" = 8bar"c"`, then A divides BC in tbe ratio ______.
Find the unit vector in the diret:tion of the vector `veca = hati + hatj + 2hatk`
In ΔABC the mid-point of the sides AB, BC and CA are respectively (l, 0, 0), (0, m, 0) and (0, 0, n). Then, `("AB"^2 + "BC"^2 + "CA"^2)/("l"^2 + "m"^2 + "n"^2)` is equal to ______.
M and N are the mid-points of the diagonals AC and BD respectively of quadrilateral ABCD, then AB + AD + CB + CD is equal to ______.
The position vectors of three consecutive vertices of a parallelogram ABCD are `A(4hati + 2hatj - 6hatk), B(5hati - 3hatj + hatk)`, and `C(12hati + 4hatj + 5hatk)`. The position vector of D is given by ______.
The position vector of points A and B are `6 bar "a" + 2 bar "b" and bar "a" - 3 bar"b"`. If the point C divided AB in the ratio 3 : 2, show that the position vector of C is `3 bar "a" - bar "b".`
If `bara, barb` and `barr` are position vectors of the points A, B and R respectively and R divides the line segment AB externally in the ratio m : n, then prove that `barr = (mbarb - nbara)/(m - n)`.
Using vector method, prove that the perpendicular bisectors of sides of a triangle are concurrent.
Find the ratio in which the point C divides segment AB, if `5bara + 4barb - 9barc = bar0`
AB and CD are two chords of a circle intersecting at right angles to each other at P. If R is the centre of the circle, prove that:
`bar(PA) + bar(PB) + bar(PC) + bar(PD) = 2bar(PR)`
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara + 2 barb and bara - 3 barb`. If point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2, then show that the position vector of C is `3bara - barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are `6bara + 2 barb` and `bara-3 barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is `3bara -barb`.
The position vector of points A and B are 6`bara + 2barb and bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3 : 2 then show that the position vector of C is 3`bara - barb`.
The position vectors of points A and B are 6`bara` + 2`barb` and `bara - 3barb`. If the point C divides AB in the ratio 3:2, then show that the position vector of C is 3`bara - b`.
