Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
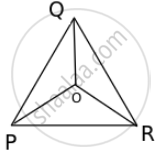
Six particles situated at the corner of a regular hexagon of side a move at a constant speed v. Each particle maintains a direction towards the particle at the next corner. Calculate the time the particles will take to meet each other.
उत्तर
A regular hexagon has a side a. Six particles situated at the corners of the hexagon are moving with a constant speed v.
As per the question, each particle maintains a direction towards the particle at the next corner. So, particles will meet at centroid O of triangle PQR. Now, at any instant, the particles will form an equilateral triangle PQR with the same centroid O.
We know that P approaches Q, Q approaches R and so on.
Now, we will consider the motion of particle P. Its velocity makes an angle of 60˚.
This component is the rate of decrease of distance PO.
Relative velocity between P and Q:
\[\vec{\text{ v } }_{\text{PQ }} = \vec{\text{v }}_P - \vec{\text{v }}_Q = \vec{\text{v}} - \vec{\text{v}} \cos 60^\circ\]
\[ = \vec{\text{v}} - \frac{\vec{\text{v}}}{2} = \frac{\vec{\text{v}}}{2}\]
\[\text{ Time } , t = \frac{\text{ Displacement }}{\text{ Velocity } }\]
\[ = \frac{a}{\text{ v }/2} = \frac{2\text{a} }{\text{v }}\]
Hence, the time taken by the particles to meet each other is \[\frac{2\text{a }}{\text{v } }\] .
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two trains A and B of length 400 m each are moving on two parallel tracks with a uniform speed of 72 km h–1 in the same direction, with A ahead of B. The driver of B decides to overtake A and accelerates by 1 m/s2. If after 50 s, the guard of B just brushes past the driver of A, what was the original distance between them?
A three-wheeler starts from rest, accelerates uniformly with 1 m s–2 on a straight road for 10 s, and then moves with uniform velocity. Plot the distance covered by the vehicle during the nth second (n = 1,2,3….) versus n. What do you expect this plot to be during accelerated motion: a straight line or a parabola?
The velocity of a particle is towards west at an instant. Its acceleration is not towards west, not towards east, not towards north and towards south. Give an example of this type of motion .
In a projectile motion the velocity
Two bullets are fired simultaneously, horizontally and with different speeds from the same place. Which bullet will hit he ground first?
A train starts from rest and moves with a constant acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 for half a minute. The brakes are then applied and the train comes to rest in one minute. Find the position(s) of the train at half the maximum speed.
A bullet going with speed 350 m/s enters a concrete wall and penetrates a distance of 5.0 cm before coming to rest. Find the deceleration.
A police jeep is chasing a culprit going on a motorbike. The motorbike crosses a turning at a speed of 72 km/h. The jeep follows it at a speed of 90 km/h, crossing the turning ten seconds later than the bike. Assuming that they travel at constant speeds, how far from the turning will the jeep catch up with the bike?
A ball is projected vertically upward with a speed of 50 m/s. Find the speed at half the maximum height. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a speed of 28 m/s.Find its velocity one second before it reaches the maximum height.
An NCC parade is going at a uniform speed of 6 km/h through a place under a berry tree on which a bird is sitting at a height of 12.1 m. At a particular instant the bird drops a berry. Which cadet (give the distance from the tree at the instant) will receive the berry on his uniform?
A ball is dropped from a height of 5 m onto a sandy floor and penetrates the sand up to 10 cm before coming to rest. Find the retardation of the ball is sand assuming it to be uniform.
A ball is thrown at a speed of 40 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Find the range of the ball. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A ball is projected from a point on the floor with a speed of 15 m/s at an angle of 60° with the horizontal. Will it hit a vertical wall 5 m away from the point of projection and perpendicular to the plane of projection without hitting the floor? Will the answer differ if the wall is 22 m away?
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. If he heads in a direction making an angle θ with the flow, find the time he takes to cross the river.
A swimmer wishes to cross a 500 m wide river flowing at 5 km/h. His speed with respect to water is 3 km/h. Find the shortest possible time to cross the river.
A ball is dropped from a building of height 45 m. Simultaneously another ball is thrown up with a speed 40 m/s. Calculate the relative speed of the balls as a function of time.
It is a common observation that rain clouds can be at about a kilometre altitude above the ground.
- If a rain drop falls from such a height freely under gravity, what will be its speed? Also calculate in km/h. ( g = 10 m/s2)
- A typical rain drop is about 4mm diameter. Momentum is mass x speed in magnitude. Estimate its momentum when it hits ground.
- Estimate the time required to flatten the drop.
- Rate of change of momentum is force. Estimate how much force such a drop would exert on you.
- Estimate the order of magnitude force on umbrella. Typical lateral separation between two rain drops is 5 cm.
(Assume that umbrella is circular and has a diameter of 1 m and cloth is not pierced through !!)
